A Quick Update from the MMEA Annual State Conference
Today (February 21, 2026) it was my pleasure to present at the Maryland Music Educators Association (MMEA) Annual State Conference in the Baltimore Convention Center.
The session was revised from past workshops at PMEA Annual and NAfME Eastern Division Conferences. Feel free to share these materials with fellow music education majors and NAfME college chapters… even hold meetings with them to sponsor group demonstrations of mock interviews to provide an audience and feedback for your practice sessions.

To-Do’s for Future Educators Seeking Employment
We have covered a lot of the concepts of “the art and science” of interviewing. As a review, here’s recap homework for anyone interested in developing better marketing, branding, and networking techniques, skills in storytelling at interviews, and improving their performance at employment screenings:
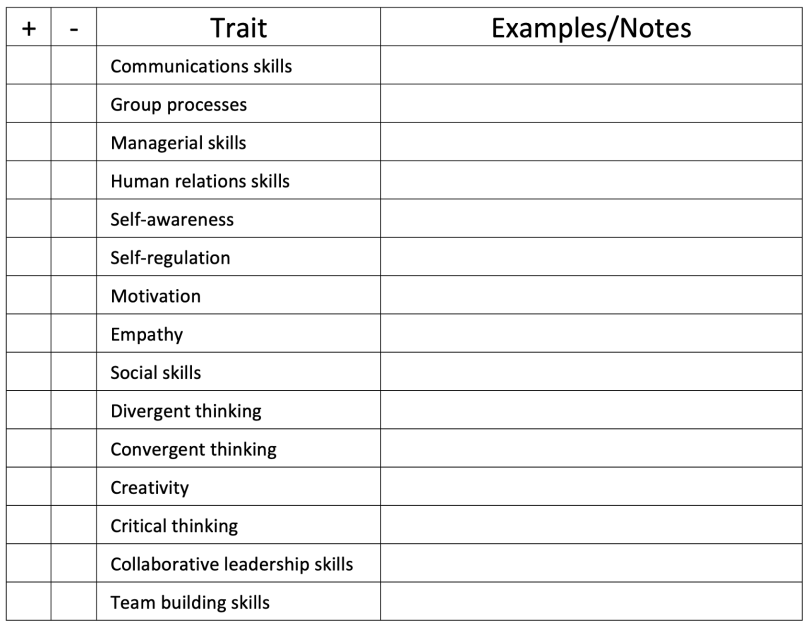
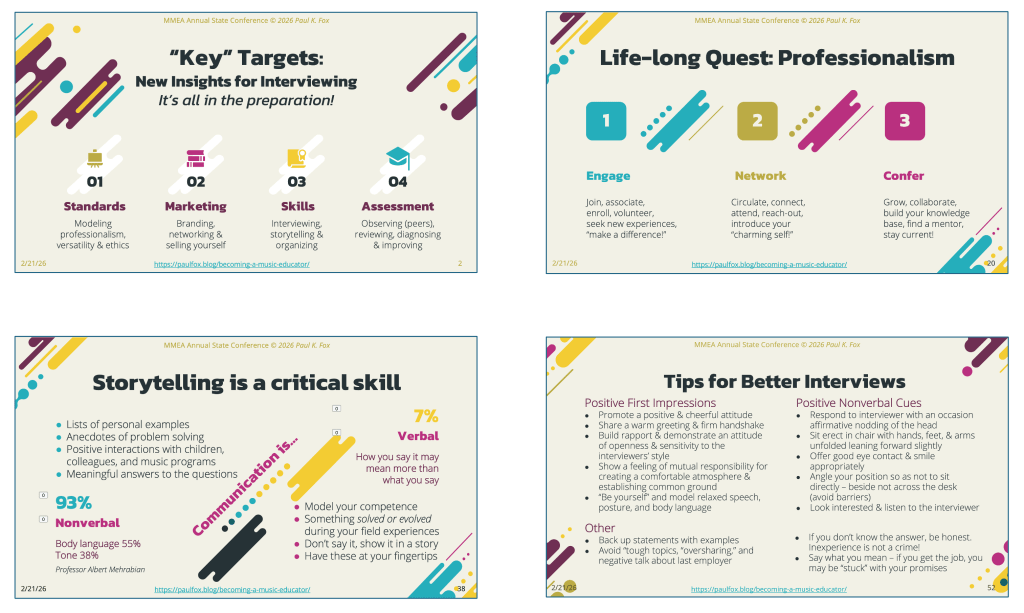
Standards: Define your personal mission, goals, and philosophy for teaching music, modeling the highest ideals of professionalism, ethics, and becoming the “total music educator.” Have you read the Model Code of Ethics for Educators brochure?
Marketing: Design and distribute a “state-of-the-art” résumé, e-portfolio, website, and business card.
Skills: Compile a list of anecdotes and true stories of you overcoming challenges, solving problems, and demonstrating “best practices” of professionalism and self-improvement.
Assessment: Practice, record, and evaluate yourself answering behavioral & typical job interview questions
Review all the links here and this updated Ultimate Interview Primer handout and slide summary from the MMEA Annual State Conference.
Sample Slides
Click here for the entire slide summary.

Follow-up Reflections — The Top Ten!
Be ready to answer these in depth and with supportive evidence and sincerity at interviews:
- What is your philosophy for the study of music and the arts in the public schools?
- Why do you want to become a teacher? What motivates you to pursue this career path?
- What should be the most important emphasis in school curriculum — the mastery of content, outcome, or process?
- What is your personal mission, goals, and planned career trajectory?
- What are your most unique and essential personality characteristics and core values? (What matters to you most?)
- What are your most unique and essential professional habits that would equip you in becoming an effective educator?
- What is your proudest professional accomplishment? Why is this important to you? How would this relate to your teaching?
- What stories about your past positive interactions with children in education settings would demonstrate you modeled care, competence, compassion, and problem solving?
- How have you evolved in becoming a qualified educator during your pre-service field experiences?
- How and when have you “collected” and practiced responses to a large number of interview questions, including S.T.A.R. (Situation/Task/Action/Results) behavioral inquiries, and then recorded and assessed yourself doing these in a mock interviews or sessions of peer reviews?

One-Stop Help
In conclusion, about a year ago, I posted this Get-a-Job Toolbox blog. Please revisit the article, scroll down below the toolkit graphic, and follow in sequence as many of the published eighteen steps as possible.
High in the Himalayan mountains lived a wise old man. Periodically, he ventured down into the local village to entertain the villagers with his special knowledge and talents. One of his skills was to psychically tell the villagers the contents in their pockets, boxes, or minds. A few young boys from the village decided to play a joke on the wise old man and discredit his special abilities. One boy came up with the idea to capture a bird and hide it in his hands. He knew of course, the wise old man would know the object in his hands was a bird. The boy devised a plan. Knowing the wise old man would correctly state the object in his hands was a bird, the boy would ask the old man if the bird was dead or alive. If the wise man said the bird was alive, the boy would crush the bird in his hands, so that when he opened his hands the bird would be dead. But, if the wise man said the bird was dead, the boy would open his hands and let the bird fly free. So no matter what the old man said, the boy would prove the old man a fraud. The following week, the wise old man came down from the mountain into the village. The boy quickly caught a bird and cupping it out of sight in his hands, walked up to the wise old man and asked, “Old man, old man, what is it that I have in my hands?” The wise old man said, “You have a bird, my son.” And he was right. The boy then asked, “Old man, old man, tell me: Is the bird alive or is it dead?” The wise old man looked at the boy, thought for a moment and said, “The bird is as you choose it to be. It’s destiny is in your hands.”
— Larry Broughton (also attributed to the Unitarian Universalist Association parable and Indian folk tale)
Indeed, regards to the preparation and practice of taking employment interviews and landing your “ideal job,” YOUR DESTINY IS IN YOUR HANDS.

A Plethora of Additional Resources
- Interviewing Boo-Boos
- Storytelling – Part 2
- Mock Interviews – Unraveling the Puzzle of Landing a Music Teacher Job
- Model Code of Ethics for Educators
- Questions for the Three Phases of Interviews
- More on Teacher Interviews
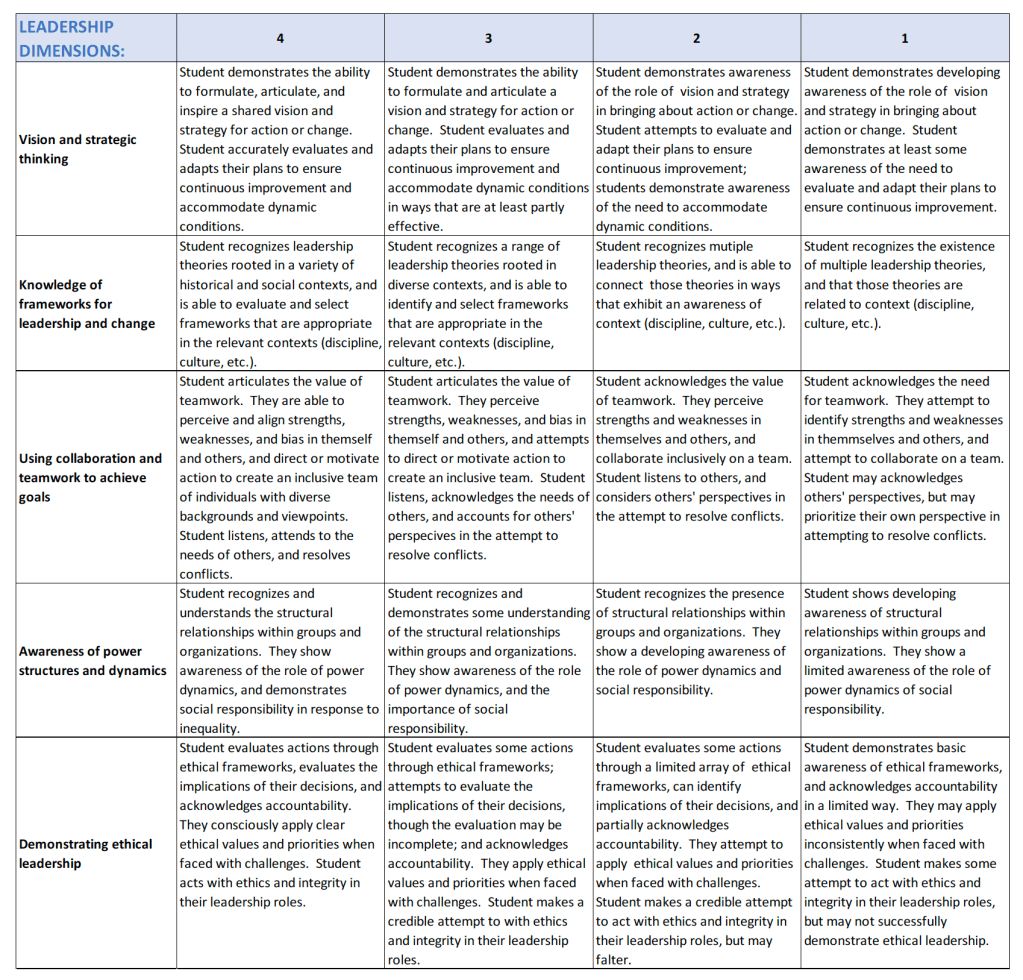
- Job Interview Rubrics
- Interviews
- The Professional Website
- Dressing for Success at Teacher Interviews
- inteREVIEWING the situation… and jobs
- Body Language & Interviewing for a Job
- 21st Century job search techniques
- Those tricky interview questions
- Networking niceties – the how-to schmooze guide
- Interview questions revisited
- Hints for the job search process
- All eyes on the job resume/music teacher resumes revisited
- Tips on personal branding
- The “alphabet soup” of current educational jargon – terms, acronyms, and trends
- S is for storytelling at interviews
- Criteria for selection of the “ideal” school teacher candidate
- A blueprint for success – Preparing for the job interview
- The do’s and don’ts of interviewing
- Planning the “perfect” professional portfolio
© 2026 Paul K. Fox