
According to the Smithsonian, 2026 is “The Year of the Fire Horse.”
The Chinese Lunar New Year begins February 17, 2026, and starts the Spring Festival season that ends fifteen days later on the evening of the Lantern Festival. The Chinese zodiac rotates through a 12-year cycle of animals and the traditional five elements: wood, fire, earth, metal, and water… The horse ushers in the seventh year of the 12-year cycle, following the Year of the Snake. Different regions across Asia celebrate Lunar New Year in many ways and may follow a different zodiac.
– SmithsonianThe Horse embodies enthusiasm, speed and fieriness, bringing a year focused on bold moves and exploration, according to Chengxin Li from Astrala. Those born in a Year of the Horse are often seen as confident, agreeable, and responsible, although they also tend to dislike being reined in by others. Celebrities born in a Year of the Horse include Nelson Mandela, Paul McCartney, Barbra Streisand, Calvin Klein, Jerry Seinfeld, Jackie Chan, John Travolta, Janet Jackson, Usher, Kobe Bryant and Jennifer Lawrence. “In their zodiac year, Horses experience highs and lows in love, work, and health. Breakthroughs are possible through persistence, while balanced self-care and steady finances ensure long-term success,” according to Sophie Song from Astrala.
– Lauren Kobley
Colligating these online sources, one might say that this could be the year we all embrace “enthusiasm,” “exploration,” “breakthroughs,” “boldness,” and “persistence.” In other words – “professional development!”
I heartily recommend you remain actively involved in your professional music/education association and attend at least one state or national conference or regional workshop every year. Yes, this suggestion is good for pre-service (collegiate or soon-to-be) educators and retirees, too! This often-repeated quote from a past issue of PMEA Retired Member Network eNEWS clearly states “the why” (“rationale” – the focal point of many keynoter Simon Sinek’s presentations) to participate in continuing professional development sessions:
For some of us, it’s a just chance to catch-up with our colleagues, see our friends, and socialize. Others are more focused and take advantage of the near-perfect opportunity to network with other professionals, perhaps seeking new working relationships, partnerships, or even employment. Many are on a look-out for newly published music, that perfect music lesson or teaching strategy, technology tools, fundraisers, advance educational venues, or much-needed equipment to purchase for our ensembles or classrooms. Most come to hear/see the “state of the art” in music education – concerts, demonstrations, keynote speeches, panel discussions, exhibits, research presentations, and workshops. PMEA’s PD Council would likely submit that the primary purpose of a conference is for professional self-improvement… What did Stephen Covey call it? His Habit #7 of “sharpening the saw” – to build a balanced program of self-renewal in the four areas of your life: physical, social/emotional, mental, and spiritual. Covey would insist we embrace “the process that empowers us to move on an upward spiral of growth and change, of continuous improvement.” So, in short, conferences help us “grow” – to revive, re-inspire, re-energize, rejuvenate, re-direct, and re-motivate all of us – pre-service, active in-service, and retired teachers towards making successful new connections, updating our knowledge and skills, and forming new goals. This is how we “keep up” with all the new standards, benchmarks, and cutting-edge advances, and meet the “movers-and-shakers,” visionaries, and leaders in the profession!
Where to go? What to see? What’s YOUR pleasure? Pick a location: Washington D.C., Baltimore, or The Poconos in Northeastern Pennsylvania! I’ll be attending all three!
DCMEA

The earliest conference workshop series on my docket for 2026 is coming up in three weeks: DCMEA Winter Conference. For out-of-town attendees, DCMEA offers a discounted hotel stay at the Line Hotel D.C.
- Date: January 30, 2026 from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- Location: Columbia Heights Education Campus
- Click here for registration link
- Click here for session schedule
- Keynote Speaker: Nationally recognized leader, educator, and advocate, NAfME Past President Scott Sheehan will present ideas to ignite your passion and commitment to a fulfilling career in music education.
I feel privileged to have been invited to present the following three sessions at DCMEA Winter Conference.

Self-Care Cookbook – Reflections, Recipes, and Resources
Time: 8:00 a.m.
Self-Care Handout
Self-Care Slide Summary
Description: The purpose of this session is to empower teachers with skills and attitudes needed to make informed decisions to promote their own lifelong health and wellbeing, and to remediate stress and burnout. With the introduction of new resources for self-assessment and study, we will explore these essential questions:
- What are suggestions, strategies, and samples for the development of a personal self-care plan?
- Why is it essential to personal health to achieve balance in our lives, and how can we achieve it?
- How does dedication to wellness impact the risk of illness, injury, and the quality of a person’s life?
- What are the consequences of our choices in terms of time and stress management?
- How do effective decision-making skills and goal setting influence healthier lifestyle choices?
This workshop will provide the takeaway of “two-for-one” follow-up slide decks: Self-Care (1.0) to foster in the individual teachers themselves the acquisition of new techniques for self-assessment, self-care goal setting, and work/life balance, and the other, Self-Care 2.0 recently presented at the PA Department of Education’s state conference SAS INSTITUTE for school leaders to cultivate in their staff better habits of health and wellness and to improve school climate and culture.

Social Media – Boon or Nemesis?
Time: 11 a.m.
Social Media Handout
Social Media Slide Summary
Description: The presentation will touch-on various legal issues, the ethical framework necessary to guide teacher decision-making and the avoidance of unacceptable “appearances or actions,” and precautions for the use of digital communications and social networks. Sample success stories, “exemplars,” and resources for the safe use of tech tools and applications of social media/remote/alternative/distance learning will be shared.
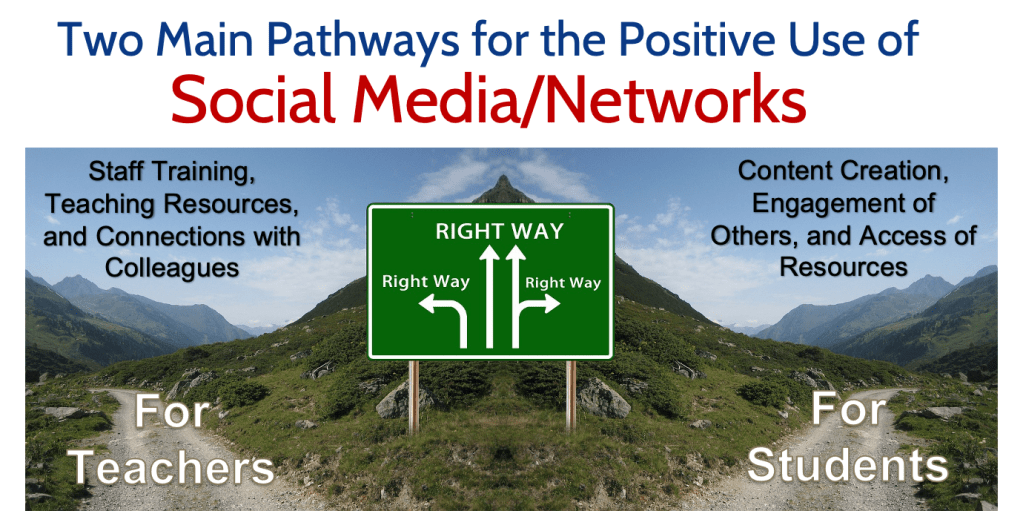
All Aboard the E3-Train! ⏤ Essential Educator Ethics…
and introducing NASDTEC’s Model Code of Ethics for Educators
Time: 1:00 p.m.
Ethics Handout
Ethics Slide Summary
Description: Teachers make thousands of decisions every day resolving conflicts in pedagogy, enforcement, resource allocation, relationships, and diversity. Many of these are “snap judgments” relying on gut feelings, intuition, past experiences, and a personal moral compass. And, although Johnny Cash may have sung “I walk the line…” in his love song, in education it is often a perilous “fine line” to maintain the standards and appearances of professionalism, integrity, and ethical codes both in and outside the school community.
This workshop will foster interactive facilitated discussions on risk assessment and resolution of ethical disputes and “conundrums” both in and outside the workplace. We will introduce the National Association of State Directors of Teacher Education and Certification Model Code of Ethics for Educators (MCEE) and empanel a mock jury of volunteer attendees to analyze and judge sample (real or hypothetical – “what would you do?”) scenarios for new perspectives in managing day-to-day decision-making in music education.

MMEA

Our next professional development journey takes us to the three-day MMEA Annual State Conference in Baltimore.
- Dates: February 20-22, 2026
- Location: Baltimore Convention Center (Friday and Saturday) and Morgan State University, Murphy Center for the Arts (Sunday)
- Click here for registration link
- Click here for session schedule
- Keynote Speaker: John Jacobson, a celebrated author and composer whose musicals have been performed by millions of children worldwide. Session is sponsored by Musicplay.

My session The Interview Clinic will be presented on Saturday, February 21 at 10:00 a.m. in Room 325. Geared to the coaching of college music majors, pre-service, unemployed, educators in transition, or those teachers seeking new positions, this workshop will provide hands-on interactive exercises to improve candidate performance at employment screenings.
Description: How do you get to Carnegie Hall? Practice, practice, practice! How do you succeed at job interviews? Practice, practice, practice! Are you looking for your first job over the next year or so? Or, are you trying to “move up” to a better position? This workshop will provide hands-on tips, tricks, techniques, and trial exercises for developing skills in professional marketing, branding, storytelling, and networking.
The valuable resource, The Ultimate Interview Primer for the Preservice Music Teacher, will be shared archiving an extensive library of supplemental self-help links to interview questions, good/bad habits at employment screenings, and additional strategies for landing the job you always wanted.


PMEA
It probably will not come as a surprise to readers of this blog that my favorite professional development venue is the Pennsylvania Music Educators Association Annual Conference… of which I have missed perhaps only three of these “celebrations” over nearly five decades of involvement in music education, all starting with my HS participation in PMEA All-State Band (tuba) and PMEA All-State Orchestra (viola). PMEA Annual Conference is the main event providing “state of the art” keynoters, clinicians, educators, expert innovators, performers, curriculum designers, and supportive vendors, and more than any other source, probably has had the greatest influence on sustaining my growth as a music educator. Like many other “diversified colleagues,” throughout my career I had to go through transitions of teaching new grade levels and content specialties (although orchestra and strings were my “thing,” new job assignments required retooling and fostering renewed skills in music theory, technology, choral, musicals, and even elementary band)… and PMEA’s professional development offerings were always my “go to!”
If you live in or near the Commonwealth, you should drop everything today and register for the PMEA Annual Conference at the Kalahari Resort in the Poconos.
- Dates: April 23-25, 2026
- Location: Kalahari Resort, Poconos, PA
- Click here for registration link
- Click here for the session schedule


I am happy to announce that I will present/facilitate several sessions at PMEA’s Scaling Heights 2026:
- April 23: Self-Care Cookbook – Reflections, Recipes, and Resources
- April 24: Retirement 101 – Retiree Stories and Strategies
- April 25: It Takes a Village – Music Booster Parent and Director Sharing Session
More details about these session will be coming in future blog posts.
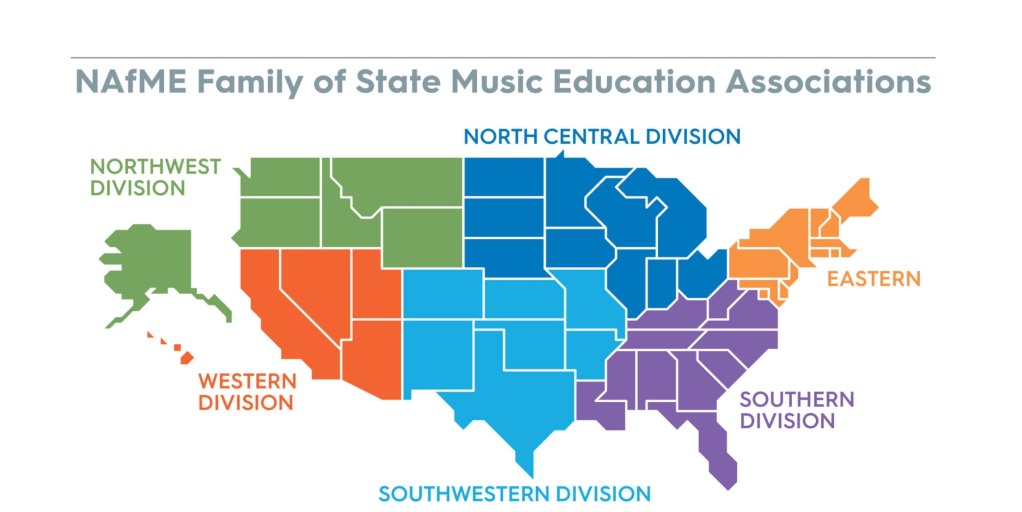
These conferences are only the tip of the iceberg! If you need to consider other MEA sites or more convenient locations to where you live, peruse the NAfME website here, where there is a quick count of more than 52 (state) music education associations, most with one or more conferences per year!
So, now are you interested in galloping or just trotting through The Year of the Fire Horse? Make a New Year’s Resolution to attend one MEA event in 2026. Apathy is not an option! Excuses will NOT be accepted!
PKF
© 2026 Paul K. Fox



















 “Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”
“Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”



 For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc.
For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc. Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library
Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library  Five tips for coaching overwhelm:
Five tips for coaching overwhelm:

 “It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”
“It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”

 Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review
Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review  Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:













 Focus
Focus

 Why even good days with your students leave you drained.
Why even good days with your students leave you drained.



 But then a group of British and dutch researchers asked an interesting question. They wondered if everyone had it backwards. Did the discomfort of physical fatigue cause the runners to think negatively, like everyone assumed, or did the runners negative thoughts make them more physically tired and sore? It was a chicken and egg question.
But then a group of British and dutch researchers asked an interesting question. They wondered if everyone had it backwards. Did the discomfort of physical fatigue cause the runners to think negatively, like everyone assumed, or did the runners negative thoughts make them more physically tired and sore? It was a chicken and egg question.
 6:30 a.m. an hour of cardio
6:30 a.m. an hour of cardio sake of the music program, add a new ensemble, schedule after-school time to teach a solo or instrumental part, and plan more weekend and evening “learning activities” or events beyond the scope of most other academic subject teachers. It was not unusual for me to be at school by 6:45 a.m., eat lunch in my car on the way to my second or third assignment as an itinerant, stop for a quick “date” and dinner out with my wife, return to school for band, orchestra, or musical practices, and not get home until 9 or or 10 p.m. As a retiree, I now ask, “What ever happened to all of this stamina and endurance?” Pushing wheel chairs only four hours a day three times a week at a local hospital, I sometimes find myself wanting to take a “power nap” when I get home! Never you fear: the healthy “calendar of a retired music teacher” is as busy (and hectic) as full-time employment… We always say, “I wonder how I ever had the time to do all of these things and work at the same time!”
sake of the music program, add a new ensemble, schedule after-school time to teach a solo or instrumental part, and plan more weekend and evening “learning activities” or events beyond the scope of most other academic subject teachers. It was not unusual for me to be at school by 6:45 a.m., eat lunch in my car on the way to my second or third assignment as an itinerant, stop for a quick “date” and dinner out with my wife, return to school for band, orchestra, or musical practices, and not get home until 9 or or 10 p.m. As a retiree, I now ask, “What ever happened to all of this stamina and endurance?” Pushing wheel chairs only four hours a day three times a week at a local hospital, I sometimes find myself wanting to take a “power nap” when I get home! Never you fear: the healthy “calendar of a retired music teacher” is as busy (and hectic) as full-time employment… We always say, “I wonder how I ever had the time to do all of these things and work at the same time!”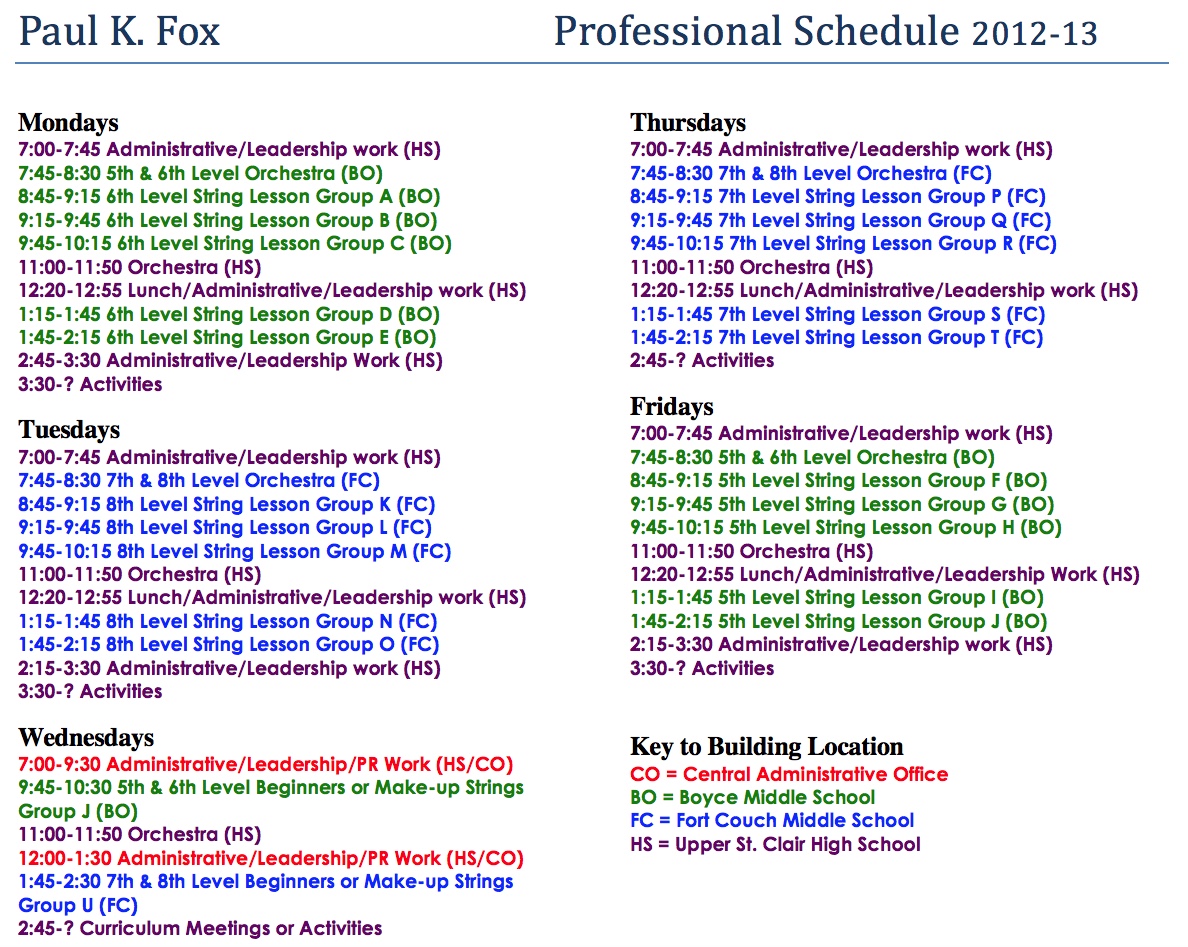
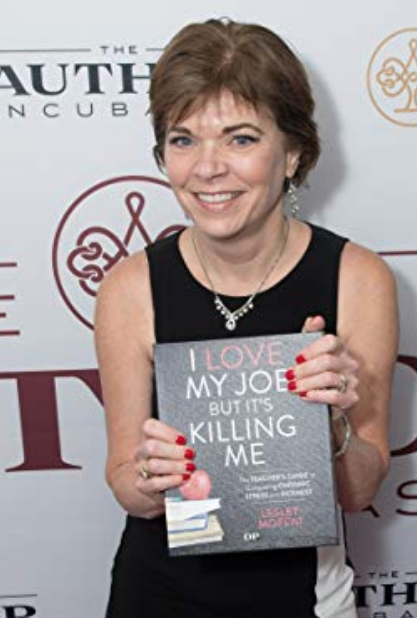







 Now in her fourth decade as a high school band director, Lesley Moffat has worked with thousands of people, helping them not only achieve musical goals (including repeated performances at Carnegie Hall, Disney Theme Parks, Royal Caribbean cruise ships, and competitions and festivals all over the US and Canada), but also teaching them how to develop the long-term life skills they need to be successful in the world.
Now in her fourth decade as a high school band director, Lesley Moffat has worked with thousands of people, helping them not only achieve musical goals (including repeated performances at Carnegie Hall, Disney Theme Parks, Royal Caribbean cruise ships, and competitions and festivals all over the US and Canada), but also teaching them how to develop the long-term life skills they need to be successful in the world.