We thought our next article in this series on music teacher health and wellness was going to center around burn-out. But then… COVID-19 struck (was this really only 3-4 months ago?), we were forced into self-isolation, and all “brick and mortar” schools closed. In the ensuing panic, we all scurried about seeking solutions to reconnect and engage our students from afar in compliance with strict shelter-in-place restrictions.
“Seemingly overnight, the world changed. Teachers and school leaders have had to revamp their entire instructional systems with, in many instances, only a day’s notice. To say many of us are experiencing whiplash, disorientation, and anxiety is an understatement.”
 “Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”
“Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”
“In these unprecedented times, teachers are rising to the occasion creatively and quickly to shift to remote learning amidst school closures. Even in a traditional classroom, it can be a challenge to support students with anxiety and trauma histories to stay calm and learn. With distance learning, this difficulty is magnified. However, there is much teachers can do to reduce anxiety in students even while teaching remotely. During this crisis, we need to prioritize students’ mental health over academics. The impact of trauma can be lifelong, so what students learn during this time ultimately won’t be as important as whether they feel safe.”
— “Maintaining Connections, Reducing Anxiety While School Is Closed” by Jessica Minahan in ASCD Educational Leadership, Summer 2020
My opinion? The Internet and other forms of media can be a godsend or a contributing factor to our feelings of malaise. The 24/7 nature and immediacy of news programs and web posts updating the statistics of new coronavirus cases, hospital admissions, deaths, shortages of personal protection equipment and respirators, unemployment numbers, and the stock market’s roller-coaster ride, have added fear, stress, and “noise” to the real problem… our ability to cope with the ramifications of this pandemic!
Well, at least a lot of dialogue has been generated “out there” about recommended remediation and “success stories.” The purpose of this blog-post is to share some of this “advice from the experts.” Many of you (I hope) may say, “This is just common sense.” True, but however “common” it is, more people than you think are not applying these principles to their own personal lives. And like the one online post that caught my eye the other day, “Teachers Are Breaking” by Jessica Lifshitz, all of us should share our anecdotes… the trials, internal struggles, and tribulations… to make it through this emergency.
Together, we are stronger!

I have been accused of being a little too emotional and I should not “feed into the negativity,” as one reader complained in reaction to one of my blogs. However, according to this article by Christina Cipriano and Marc Brackett, “emotions drive effective teaching and learning, the decisions educators make, classroom and school climate, and educator well-being.”
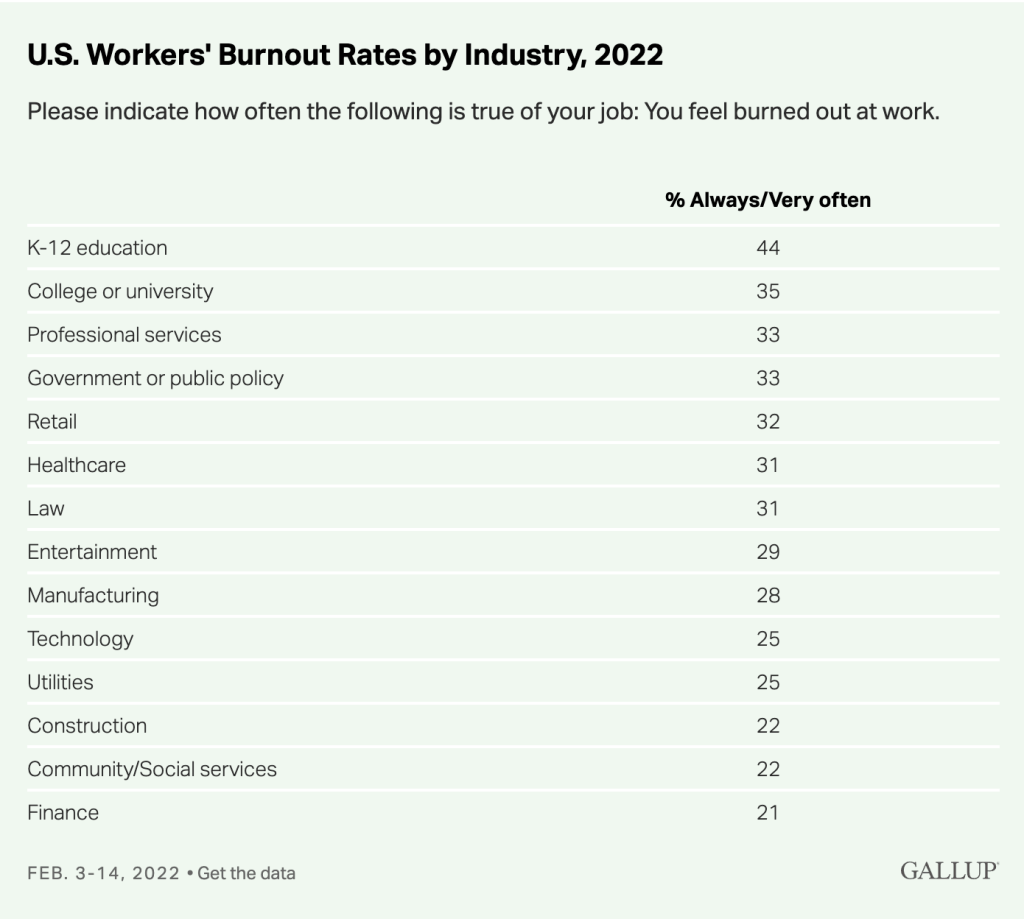
“At the end of March, our team at the Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, along with our colleagues at the Collaborative for Social Emotional and Academic Learning, known as CASEL, launched a survey to unpack the emotional lives of teachers during the COVID-19 crisis.”
“In the span of just three days, over 5,000 U.S. teachers responded to the survey. We asked them to describe, in their own words, the three most frequent emotions they felt each day.”
“The five most-mentioned feelings among all teachers were: anxious, fearful, worried, overwhelmed and sad. Anxiety, by far, was the most frequently mentioned emotion.”
— Navigating Uncertain Times: How Schools Can Cope With Coronavirus
Almost in unison, the strategies that seem to be echoed most often by medical and mental health professionals, educators on the front line, and even technology specialists, are outlined by this “wellness map of to-do’s!”
- Don’t obsess. Calm yourself. Set priorities.
- Connect and communicate often with your family members and your students.
- Set and maintain boundaries.
- Practice mindfulness.
- Take the necessary steps to maintain your own physical and mental health!

Avoiding Becoming Overwhelmed
As a retiree, I “only” lost the spring season of my community youth orchestra to this crisis. In my position as state chair of the PMEA Council Teacher Training, Recruitment, and Retention (PMEA Council TTRR), I tried to soothe the “hysteria” of many of my still-working friends and colleagues who were grappling with the instantaneous roll-out of distance learning. After researching online music education resources, we were able to place countless links on the PMEA Council TTRR website (here). After 7+ weeks, one of our “omnibus Google Docs” has grown to 15+ pages and more than 225 separate sources of virtual, remote, and alternative music learning media and methods.
 For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc.
For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc.
Take a deep breath! Focus! Prioritize your goals. What are you trying to accomplish? Don’t try to consume all of the available resources “out there,” nor use every application or online lesson that you find on Facebook groups like https://www.facebook.com/groups/mecol/. What was it my mother used to say at the dinner table? “Sip and chew slowly… don’t gulp!” Take away what might help your situation, but approach anything brand new in moderation!
 Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library here, the aforementioned Facebook group and others, and if you already have a membership in PMEA, this website.
Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library here, the aforementioned Facebook group and others, and if you already have a membership in PMEA, this website.
BUT… plan to take away ONLY one or two new “teaching tools” from each session… maybe consider trying-out one new app or lesson idea every other week?
As if to anticipate our needs, more than a year ago, Elena Aguilar published the in-depth piece “How to Coach the Overwhelmed Teacher” in Education Week blog, summarizing excellent stress-reduction treatments. (Share these if you think they will help you or some else! Read the entire article for more detail!)
 Five tips for coaching overwhelm:
Five tips for coaching overwhelm:
- Describe it.
- Recall previous experiences.
- Identify one tiny next step.
- Listen.
- Plan for action.
“When coaching someone experiencing strong emotions, it’s important to know the signs and indicators of depression and anxiety disorders. Emotions can turn into moods, and if moods hang around long enough, they may become depression or an anxiety disorder. People who feel overwhelmed a great deal may be experiencing depression, whereas those who are ‘stressed’ a lot may be experiencing anxiety. This resource, AppD Depression_Anxiety.pdf, can be offered to your coachees or used to consider whether someone may need professional help.”
“When coaching any strong emotion, it’s useful to remember that emotions can be guides to self-understanding. They are a normal part of being a human being, and strong emotions show up to get us to pay attention to what’s going on. We can welcome strong emotions—in ourselves and in our coachees—and explore them to gain insight into ourselves and humans and educators.” — Elena Aguilar

Making Connections
Your loved-ones and friends probably need you now more than ever!
And, a myriad of research supports the assertion that social connections significantly improve our own physical and mental health and emotional well-being, such as published by the “Center of Compassion & Altruism Research & Education” of the Stanford Medical School:
“Strong social connection leads to a 50% increased chance of longevity, strengthens your immune system (research by Steve Cole shows that genes impacted by loneliness also code for immune function and inflammation), helps you recover from disease faster, [and] may even lengthen your life!”
“People who feel more connected to others have lower levels of anxiety and depression. Moreover, studies show they also have higher self-esteem, greater empathy for others, are more trusting and cooperative and, as a consequence, others are more open to trusting and cooperating with them. In other words, social connectedness generates a positive feedback loop of social, emotional and physical well-being.” — Dr. Emma Seppala
There’s even evidence that “human touch” and close connections with other people increase our body’s levels of the beneficial hormones serotonin and cortisol.
Just more common sense? Right? Probably!

The first thing I did during that initial announcement of school/activity closures was to reach-out to my “musical kids.” Many music directors told me they quickly sponsored a Zoom/Google Hangout meeting of their ensemble members, mostly just to check-in with their players or singers and get everyone “on board” for future online interactions.
Perhaps COVID-19 has made me a better “citizen,” too. Much more frequently, I now call or text a friend, colleague, volunteer co-worker, or neighbor to see how they are doing. It’s terrible to admit that it took a world disaster to improve my interpersonal communications skills!
Finally, here’s a good “recap.” In spite of the need for social distancing, these examples of “safe connections” are suggested by Jennifer Wickham from The Mayo Clinic:
- Use electronics to stay in contact with friends, neighbors and loved ones. This could include using video-conference programs, making voice calls instead of sending texts, or talking with a neighbor through windows while maintaining a safe distance.
- Spend quality time with the people you live with, such as playing board games or completing an indoor project.
- Make a family meal or dessert recipe that reminds you of friends or family you are unable to visit, and then call them to tell them about it. This way, you get an experience of internal and external connection.
- Write in a journal about your experiences during this time of social distancing. Not only will this help you sort out what you are thinking and feeling, but also it can be shared going forward as a way for future generations to connect with the past.

Setting Boundaries
Something else I admit to NOT doing!
“Going Google,” “exploring e-learning,” or “doing digital” – it is easy to get carried away and not notice you just spent 12 hours in-a-row of “screen time” participating in online meetings or creating new remote learning opportunities for your music students. Exactly when are your classroom and office hours? You are likely pushing yourself too hard, even in your pajamas! This insane pace will only promote other health concerns!
The foresight of Elisa Janson Jones was evident for writing this in her blog “7 Self-Care Strategies to Prevent Burnout” back in September 2018 before the pandemic:
 “It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”
“It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”
“We may find pride in saying we worked 60 hours this week, flaunting to our friends that we got to school in the dark and left in the dark. Perhaps we find self-importance in their pity and admiration.”
“However, to thrive in our profession, we must remember that teaching music is our career, not our entire life. Hobbies, families, volunteering, and other ways we contribute to our communities and our homes are also aspects of who we are.”
“Setting clear boundaries between when we are working for our paycheck and when we are working for ourselves helps us carve out space where we offer ourselves time to be free of obligations and burdens of our career. Whether it’s a few hours per day, a full day per week, or both, setting strict boundaries for when you’re on-the-clock and when you’re off is essential.” — Elisa Janson Jones

Mindfulness and “Living” in the Present
Another concept that Elisa Janson Jones covered in her Smartmusic blog: mindfulness.
Now is the time for a little nonjudgmental “free reflection,” or what the psychologists call the best practice of “mindfulness” – a focus with full attention on your thoughts, feelings, and sensations “in the moment.” I think the “Teaching with Orff” website really nailed it in the article “7 Self Care Tips for Quarantined Music Teachers.” Read co-author Zoe Kumagai’s examples of affirmations: “How do I want to feel today?”
- I allow myself time and space to reflect.
- My mind is aware of the present.
- My heart feels compassionate and is full of love.
- My mind is stimulated by books, stories, art, scholarly articles, music that inspire me to be my best self.
- I maintain boundaries with technology and intake of the news.
- My body is free to dance.
- My voice is clear to sing, laugh and converse authentically.
According to this Harvard Medical HelpGuide, the habits and techniques of mindfulness can improve well-being, physical health, and mental health:
“There is more than one way to practice mindfulness, but the goal of any mindfulness technique is to achieve a state of alert, focused relaxation by deliberately paying attention to thoughts and sensations without judgment… Allow thoughts to come and go without judgment and return to your focus on breath or mantra.” — HelpGuide
Band director, best-selling author, and acclaimed clinician Lesley Moffat devoted an entire chapter to mindfulness in her book I Love My Job But It’s Killing Me. You know what they say, “What’s good for the goose is good for the gander.” After learning the techniques for herself, she adopted mindfulness practice at the beginning of each band rehearsal for her students, a 4-5 minute routine of guided breathing and relaxation exercises leading up to the daily warmup chorale.

I love the symbolism in her “snow globe” analogy:
“Just like a snow globe that’s been shaken up, it takes time for your mind and body to settle down. If you try to get the snow globe to settle down while you’re still holding it and carrying on with your regular activities, the snow may fall slower, but it won’t completely stop and allow you to see the objects in the snow globe. You must allow it to be completely still long enough for the water to stop swirling and the glitter to follow the pull of gravity and settle on the bottom. It only takes a matter of minutes until it settles, revealing the magical scene inside, and the very glitter that was covering up the view when it was moving around has become a lovely blanket of snow that grounds the scene in the snow globe. But without a few minutes of stillness, it is impossible for it to become completely settled. So it goes with a mindfulness practice. Your mind and body needs time to go from hyper-speed to a pace that serves you well, a place where you have space to think – and space to not think. That begins by bringing stillness to your body and to your mind. Easy to say – hard to do… until you practice it every day and it becomes habit.” — Lesley Moffat
 Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review here.) It serves as a true treasure-house of practical applications for de-stressing and re-centering your life. Her “mPower Method of Meals, Movement, Music, and Mindfulness” may be the solution to improving your situation.
Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review here.) It serves as a true treasure-house of practical applications for de-stressing and re-centering your life. Her “mPower Method of Meals, Movement, Music, and Mindfulness” may be the solution to improving your situation.
FYI, her next book, Love the Job, Lose the Stress, is on the way. You can request an advance e-copy here.
“Do as I Say… Don’t Do as I Do!”
The worst part of this? We seldom take our own advice. Hey teacher, “heal thyself,” and “practice what you preach.” Taking care of our children or elderly relatives, we are probably the last to comply with the tenets of our own sermons on health and wellness.
Lesley Moffat also devoted a chapter in her book to the airline safety bulletin “Put On Your Own Oxygen Mask First.” You cannot take care of someone else (your family members or your music students) unless you first take care of yourself!
 Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Hydrate.
- Get enough sleep.
- Exercise daily.
- “Flex your brain.”
The latter “exercising your mind” is referenced in the Teaching with Orff website, and is a frequent emphasis on my blog-site (with examples here, here, and here). Pursue your own avenues of creative self-expression, and grow and learn something new every day!
According to charitable organization Waterford.org, the definition of “self-care” is “any action that you use to improve your health and well-being.” They cite extensive research from the National Institute of Mental Illness (NAMI), corroborating the statement that there are six elements to self-care:
- Physical
- Psychological
- Emotional
- Spiritual
- Social
- Professional

And, as explained in the article “Why Teacher Self-Care Matters, and How to Practice Self-Care in Your School,” self-care is not about selfishness.
“Self-care is an important component of a teacher’s mental health, but there are misconceptions about what it is. It’s common for educators to dismiss the self-care movement as ‘selfish’ or ‘superficial.’ But for teachers, self-care is so much more than breakfast in bed or treating yourself to a spa day. It’s about taking care of your health so that you’re prepared to be the best teacher you can be for yourself and your students.”
— Waterford.org
These endorsements probably represent just “the tip of the iceberg!” Peruse all of the resources listed below. In addition, perhaps we should take a close look at Alex Wiggin’s ASCD article, “A Brave New World: A Teacher’s Take on Surviving Distance Learning” (Educational Leadership, Summer 2020), considering the adoption of these four lessons learned from the past four months:
- Relying on a team reduces work and stress.
- Connecting with students boosts morale.
- Learning new technology isn’t so bad.
- Model being a life-long learner
I predict that the hardest part, coming to the end of May and the completion of our first-ever “virtual spring semester,” is coming to grips with our “fear of the unknown!” At the date of this writing, no one really knows when “we” are going back to “in person” schools, how we will resume large group music instruction like band, choir, or orchestra rehearsals, and what will the “new normal” look like to successfully “move on!”
Summer break is just around the corner… a good time to stop and reflect! And yes, we will make it through this.
Please stay safe! PKF

References
© 2020 Paul K. Fox
Photo credits (in order)
From Pixabay.com



























































 “Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”
“Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”



 For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc.
For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc. Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library
Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library  Five tips for coaching overwhelm:
Five tips for coaching overwhelm:


 “It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”
“It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”

 Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review
Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review  Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before: