Ask not what NAfME or your state MEA can do for you, but what YOU, a retiree, can do for your professional association and music education.
– An adaptation of the famous excerpt from the 35th U.S. President John F. Kennedy’s inaugural address of January 20, 1961.

Surfing the ‘Net, I found an appropriate acronym for R.E.T.I.R.E. by Tangled Tulip Designs in pinterest – Relax, Entertain, Travel, Indulge, Read and Enjoy! Most retirees would probably agree! The cessation of full-time employment may offer a great release from the day-to-day stress and drudgery of the job and the freedom to venture out, self-reinvent, make future goals, nurture relationships, and explore new personal growth opportunities.
Many attribute embracing a career in music education as “a calling” as opposed to just a form of employment or livelihood. From my experience, I have witnessed that most music educators are passionate for the cause of fostering creative self-expression in their students, more of a 24/7 mission, bringing intense focus and dedication to their lifework.
More to the point: Do we ever truly retire from making music ourselves and fostering this love in others?

THE “WHY!” Retirees matter and are critically needed!
One of my favorite inspirational speakers (Simon Sinek) would say, “start with the WHY!” WHY is this discussion on professional engagement of retired educators so important today?
- Their need: An informal poll of my former local educators and administrators revealed that half of them “hate retirement!” According to Dr. Robert P. Delamontagne in his book Retiring Mind (Fairview Imprints), “50% of retirees will suffer some form of acute emotional distress. This is potentially a very large problem given the fact that 10,000 people are becoming eligible for Social Security every day for the next 20 years in the US alone.” Remember this statistic the next time a senior citizen cuts you off on the road or bangs a shopping cart into your leg at the checkout!
- Our need: We are facing shortages of qualified teaching candidates across the country with unfilled openings in public school music positions and the critical need of training/mentoring the new hires.
- Society’s need: All of our voices should be combined to support the advocacy of music education, actively promoting access to school music by sharing its academic and social benefits with decision-makers, building relationships with administrators and policymakers, and utilizing resources from organizations like NAfME and the NAMM Foundation.
Despite its proven benefits, music education is often the first program to face budget cuts in schools. This is especially concerning in underserved communities, where access to music programs can be life-changing. Now more than ever, we must advocate for music education to ensure that every child has the opportunity to experience its benefits. Investing in music education is an investment in the future of our communities — helping to cultivate the next generation of creative, resilient, and innovative leaders.
– “Why Music Education Matters More Now Than Ever” by Music Will, February 2025
For eleven years (and counting), I serve as the Pennsylvania Music Educators Association (PMEA) Retired Member State Coordinator, as well as the Past State Chair (current member) of the PMEA Council for Teacher Training, Recruitment and Retention. I believe my responsibility to the state association is two-fold:
- Assist soon-to-retire professionals in achieving a smooth transition to a happy and satisfying retirement; to help them cope with the commonly-experienced emotional ups-and-downs of this life passage, wrestling with the question “what do you want to be or do when you grow up?” and making new life lesson plans and personal goals.
- Reach out to and build meaningful connections with retirees in order to fully engage them towards becoming active in their professional association; to recount, represent, and revitalize the activities of our post full-time employed music educators.
This article proposes a roadmap of crucial pathways to help music teachers approach “retirement bliss” while tapping into their hard-earned knowledge, strengths, and experiences by cultivating the benefits of their renewed participation in our professional associations.

What can NAfME and State MEAs offer retirees?
You have devoted your entire life to inspiring the development of personal artistry and “ah-ha” musical moments in others. Now it is your turn to reap the benefits (and privileges) of this commitment to the profession. NAfME and your MEAs can provide the resources and motivation of “sharing and caring,” directing retirees “places to go, people to meet, and things to do” for fulfilling that “next chapter” or (perhaps better terms) the “refirement” or “rewirement” of senior living.
Do you feel “needed” and know you “make a difference?” Research has shown that the one of the most important motivators for involvement in a professional association is that its members recognize that they are essential to its success. This quote is from Revitalizing Retirement: Reshaping Your Identity, Relationships, and Purpose by Nancy Schlossberg, attributed to Rosenberg/McCullough:
“It has been suggested that one problem of retirement is that one no longer matters; others no longer depend on us… The reward of retirement, involving a surcease from labor, can be the punishment of not mattering. Existence loses its point and savor when one no longer makes a difference.”
Most people who are one to five years away from “pulling their pin” and putting in their walking papers “do not know what they do not know.” Experts agree: “Retirement preparation is not only about the money!” Our silver-haired colleagues who have already Crossed the Rubicon and are now “living the dream” in retirement can share their trials, tribulations, and (more importantly) numerous success stories about coping with this transition!

NAfME, PMEA and this paulfox.blog/for-retirees site have archived an exhaustive number of self-help articles. Check out this omnibus NAfME blog “Retirement Prep Top-Ten Treasures.”
The benefits of retired MEA membership are numerous. Besides providing helpful transitioning advice, these advantages also come to mind:
- Answers to questions like “What have you always wanted to sing, compose, play, record, conduct, write, publish or present?” and “Where can I share my hard-won expertise and help others in the field?”
- Networks and contacts to help you develop “encore careers” in other musical or educational arenas (e.g., higher education, music industry, festival organization, travel/tour planning, composition, guest conducting, private studio teaching, church music, etc.)
- Opportunities to “rekindle your expressiveness” by participation in adult community or full/part time performance groups (playing “gigs”)
- Places to go/things to see/hear: NAfME/MEA conferences, workshops, and concerts
- Exclusive discounts and other benefits (reduced dues and registration fees)

What can retirees offer NAfME and their state MEA?
The relationship of active and retired membership in our MEAs is symbiotic. We know from the history of our associations, “giving back to the profession” remains a high priority with most retirees. This may come in many forms and settings:
- Leadership or membership in local, state, or national MEA/NAfME office, staff, advisor, or council/committee position
- Advocates for the promotion of music education to local and state government officials
- Service as presiding chair or member of the conference or workshop planning committee
- Service as evaluator of performance groups, conference sessions, or articles for publication
- Judges of local/state MEA adjudication or commercial festival
- Accompanists, coaches, arrangers, or guest conductors for festivals or school/community groups
- Services to the local music teacher in private teaching, piano playing, marching band charting, sectional coaching, choreography, music technology, instrumental repair, stage tech, etc.
- Writers for state MEA and NAfME publications and blog sites
- Contributors to online music education forums or the NAfME Connections
- Donors to and/or fund-raisers of music education charitable projects, scholarship initiatives, etc.

The PMEA Model of Retired Member Participation


PMEA values the vast wealth of experience and contributions of our retired members. We’re proud of the many programs we offer to retirees and invite you to visit our website to peruse additional information and sample digital newsletters and articles.
Retired members in Pennsylvania are involved in:
- PMEA elected and appointed offices, staff, committee chairs, and membership on councils
- PMEA Strategic Plan and Bylaws, Conference Planning, and other state/regional committees
- Retired Resource Registry* (informal mentoring for new teachers and transfers)
- How-to-Retire Webinar, Prepping for Retirement, and the Ultimate Retiree Resource Guide
- Retired Member Breakfast at PMEA Annual Conference
- Retirement 101 (The Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How) session at PMEA Annual Conference (training for all members retiring or soon-to-retire)
- Maintenance of PA Community Band, Chorus, Orchestra, and Theater group catalogs
- Maintenance of PMEA member compositions library
- Mock Job Interview Committee for music education majors
- Coffee & Conversations informal “ask an expert” lounge at PMEA Annual Conference
- Volunteering as presiding chairs for sessions and registration aides at conferences/workshops
- Pool of conference clinicians, guest lecturers, and members on discussion panels
- Participation in “Sponsor a Collegiate to Attend the Conference” campaigns
- All-State Program Patron, or contributor to the annual Irene Christman Scholarship or Margaret Bauer Grant programs.
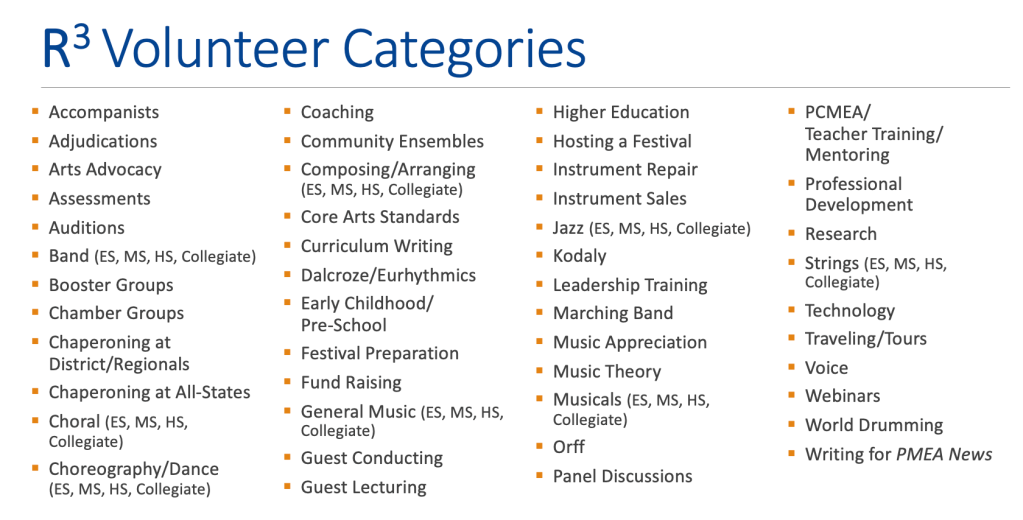
*During their annual membership registration, PMEA Retired Members may choose to sign-up for the R3 Retired Member Registry (above volunteer categories) to become available to informally offer advice to college music education majors, new hires, transfers, and newcomers to any music specialty. R3 members may handle inquiries like “What warm-up would you recommend for my middle school choir?” OR “Do you have an idea for an elementary string ensemble concert opener?” OR “How do you teach improvisation… steady beat… breath support?”
The other option with more time commitment is that Retired Members can be officially “trained” as a PMEA Mentor and be assigned to specific individuals who request assistance in their early career assignments.

Coda
How can we help?
What is the future of retired music educator professional engagement? In a word: connections!
Last month, I reached out to Elizabeth Welsh Lasko, NAfME Assistant Executive Director for Membership, Organizational Development, and Marketing Communications and “volunteered” OUR assistance. I suggested that, in keeping with the NAfME 2022 Vision Statement – “…an association where all people are heard, seen, and feel they belong throughout their lifelong experiences in music” – we should all intentionally recruit more hands-on involvement of our retirees. I pointed out that in the late 1980s, we had a Music Educators National Conference (MENC) Committee for Retired Members led by a National Chairman who served on the NAfME National Assembly. (An excellent booklet, TIPS: Retirement for Music Educators, Copyright © 1989 MENC, was compiled by A. Verne Wilson, then the Past National Chairman of the MENC Committee for Retired Music Educators.)
Ms. Lasko encouraged me to “reach out to retirees” beginning with this article. At the next NAfME Eastern Division Conference, I plan to hold a meeting of retired members, and also connect with all state MEA retired member coordinators (those states who have them). We’re available and on the move! Let’s collaborate and share our resources!

Finally, just for fun, I recently posted the blog “For Book Lovers – Retired or Not” on NAfME Connections (formerly called Amplify). There are already 1,810 members in the NAfME “Retired Members Community.” Please JOIN US! Using this forum, get in touch with me, and respond with YOUR OWN retirement stories, strategies, perspectives on this “life passage,” and more ideas to grow the professional engagement of our music teacher retirees.
Happy trails!
© 2025 Paul K. Fox





















































 In the category of “things I wishes someone would have told me before I was hired to be a school music educator,” the inspirational book, My Many Hats: Juggling the Diverse Demands of a Music Teacher by Richard Weymuth, is a recommended “first stop” and easy “quick-read.” Published by Heritage Music Press (2005), the 130-page paperback serves as an excellent summary of the attributes (or “hats”) of a “master music teacher.” Based on the photos in his work (great “props”), I would have loved to have seen Weymuth’s conference presentations in person as he donned each hat symbolizing the necessary skill-set for a successful educator.
In the category of “things I wishes someone would have told me before I was hired to be a school music educator,” the inspirational book, My Many Hats: Juggling the Diverse Demands of a Music Teacher by Richard Weymuth, is a recommended “first stop” and easy “quick-read.” Published by Heritage Music Press (2005), the 130-page paperback serves as an excellent summary of the attributes (or “hats”) of a “master music teacher.” Based on the photos in his work (great “props”), I would have loved to have seen Weymuth’s conference presentations in person as he donned each hat symbolizing the necessary skill-set for a successful educator.
 Next, I would like to direct pre-service and new music teachers to Case Studies in Music Education by Frank Abrahams and Paul D. Head. This would be an invaluable aid to “facilitate dialogue, problem posing, and problem solving” from college students (in methods classes?) and “rookie” teachers to veteran educators.
Next, I would like to direct pre-service and new music teachers to Case Studies in Music Education by Frank Abrahams and Paul D. Head. This would be an invaluable aid to “facilitate dialogue, problem posing, and problem solving” from college students (in methods classes?) and “rookie” teachers to veteran educators.
 His chapters are organized into six tips:
His chapters are organized into six tips: The first thing I want you to do (and you don’t even have to be a member of NAfME yet, although you should be!) is to take at least a half-hour, scroll down, and read through numerous NAfME “Music in a Minuet” blog-posts, bookmarking any you want to return to at a later date. Go to
The first thing I want you to do (and you don’t even have to be a member of NAfME yet, although you should be!) is to take at least a half-hour, scroll down, and read through numerous NAfME “Music in a Minuet” blog-posts, bookmarking any you want to return to at a later date. Go to 





 The purpose of this short SHJO “Series to Share” is to get you started with some basic “how-to steps” to learn how to conduct. Truly, for success in directing an ensemble, the only thing you need to do is “give it a try” and practice those beat patterns with your favorite musical selections. During the Saturday SHJO rehearsals in December, we will give you the opportunity to direct the entire group and provide you a few hints!
The purpose of this short SHJO “Series to Share” is to get you started with some basic “how-to steps” to learn how to conduct. Truly, for success in directing an ensemble, the only thing you need to do is “give it a try” and practice those beat patterns with your favorite musical selections. During the Saturday SHJO rehearsals in December, we will give you the opportunity to direct the entire group and provide you a few hints! The mission of South Hills Junior Orchestra, which rehearses and performs at the Upper St. Clair High School in Pittsburgh, PA, is to support and nurture local school band and orchestra programs, to develop knowledge, understanding, performance skills, and an appreciation of music, to increase an individual member’s self-esteem and self-motivation, and to continue to advance a life-long study of music. Members of the Orchestra learn, grow, and achieve positions of leadership to serve their fellow members.
The mission of South Hills Junior Orchestra, which rehearses and performs at the Upper St. Clair High School in Pittsburgh, PA, is to support and nurture local school band and orchestra programs, to develop knowledge, understanding, performance skills, and an appreciation of music, to increase an individual member’s self-esteem and self-motivation, and to continue to advance a life-long study of music. Members of the Orchestra learn, grow, and achieve positions of leadership to serve their fellow members.
 Before long, you will shed the label and function of a “college student” (although still remaining a life-long learner… and never stop the quest for new knowledge and self-improvement!). The focus will shift from YOU to YOUR STUDENTS. The prerequisites for a career in education are unique and do not resemble the same challenges as success in business, manufacturing, retail, service industry, or becoming an entrepreneur, blue-collar worker, or even a composer or professional musician. The sooner you realize these are world’s apart, the better, and now is the time to finish your major and life-changing transformation to… a professional music educator.
Before long, you will shed the label and function of a “college student” (although still remaining a life-long learner… and never stop the quest for new knowledge and self-improvement!). The focus will shift from YOU to YOUR STUDENTS. The prerequisites for a career in education are unique and do not resemble the same challenges as success in business, manufacturing, retail, service industry, or becoming an entrepreneur, blue-collar worker, or even a composer or professional musician. The sooner you realize these are world’s apart, the better, and now is the time to finish your major and life-changing transformation to… a professional music educator.
 Updates self with “constant education” and retooling
Updates self with “constant education” and retooling Cooperation
Cooperation
 National Association of State Directors of Teacher Education and Certification proposes these principles:
National Association of State Directors of Teacher Education and Certification proposes these principles: Here’s another query. What five groups of people are both “professionals” and “fiduciaries…” and have a legal responsibility to serve the best interests of their “clients?” The answer is… doctors/nurses, lawyers, counselors (both mental health and investment), the clergy, and… teachers.
Here’s another query. What five groups of people are both “professionals” and “fiduciaries…” and have a legal responsibility to serve the best interests of their “clients?” The answer is… doctors/nurses, lawyers, counselors (both mental health and investment), the clergy, and… teachers.  Although teachers seem to be the only one of these who DO NOT have formal pre- or in-service ethics training, and our “charges” represent a “captive audience,” our duty is clear: to act as a fiduciary for our students’ best interest, and to create and maintain a safe environment for them at all times.
Although teachers seem to be the only one of these who DO NOT have formal pre- or in-service ethics training, and our “charges” represent a “captive audience,” our duty is clear: to act as a fiduciary for our students’ best interest, and to create and maintain a safe environment for them at all times.
 What do you believe about teaching?
What do you believe about teaching? Take time to peruse these and others. Most of these sites also offer excellent examples of personal branding and marketing of the prospective job hunters’ experiences, skills, and achievements… material for our next blog on this topic.
Take time to peruse these and others. Most of these sites also offer excellent examples of personal branding and marketing of the prospective job hunters’ experiences, skills, and achievements… material for our next blog on this topic.

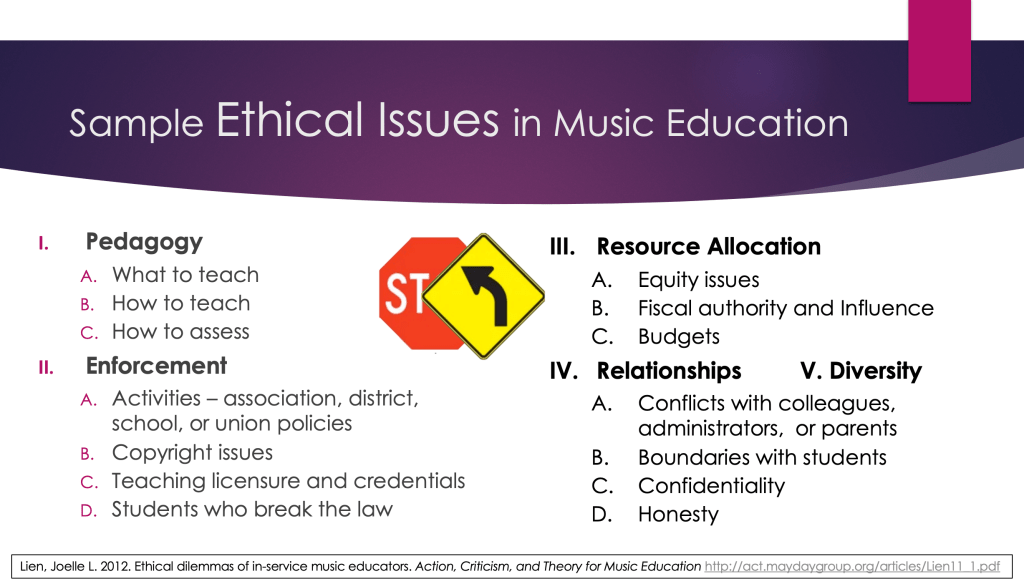
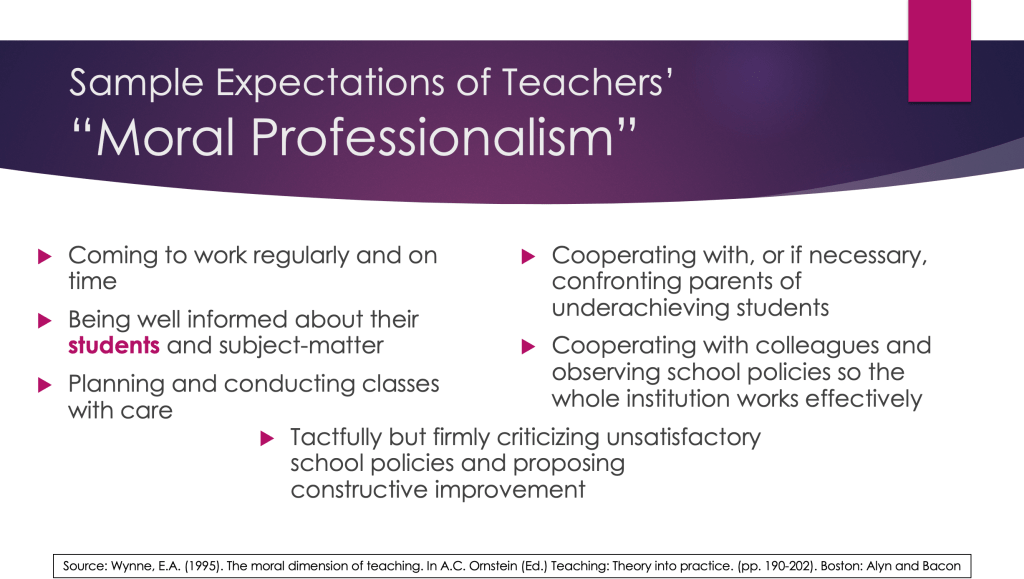
 Educators are among the singular professions which have a “fiduciary” responsibility. The term “fiduciary” can be defined as “a person or organization that owes to another the duties of good faith and trust, the highest legal duty of one party to another, and being bound ethically to act in the other’s best interests.” Joining doctors, lawyers, clergy, and mental health therapists, educators ascribe to the highest standards of training, moral decision-making (“code of ethics”), behavior (“code of conduct”), and self-regulation and assessment of the “best practices” regarding the mastery of skills and subject areas necessary to their field. However, unlike these other professionals, teachers do not receive regular and systematic pre- and in-service training on ethics, and our “clients” are a “captive audience.” Regardless, the duty of all teachers is to act as a fiduciary in their students’ best interest and to create and maintain a safe environment for them at all times.
Educators are among the singular professions which have a “fiduciary” responsibility. The term “fiduciary” can be defined as “a person or organization that owes to another the duties of good faith and trust, the highest legal duty of one party to another, and being bound ethically to act in the other’s best interests.” Joining doctors, lawyers, clergy, and mental health therapists, educators ascribe to the highest standards of training, moral decision-making (“code of ethics”), behavior (“code of conduct”), and self-regulation and assessment of the “best practices” regarding the mastery of skills and subject areas necessary to their field. However, unlike these other professionals, teachers do not receive regular and systematic pre- and in-service training on ethics, and our “clients” are a “captive audience.” Regardless, the duty of all teachers is to act as a fiduciary in their students’ best interest and to create and maintain a safe environment for them at all times.
 Always looking for the signs of…
Always looking for the signs of… Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 provides data privacy and security provisions for safeguarding medical information.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 provides data privacy and security provisions for safeguarding medical information.
 Proponents of this belief will tell you to go ahead and stick your neck out, feel free to do something “for the good of the order,” and later “beg for forgiveness” if/when it goes south and your administrators say they do not approve.
Proponents of this belief will tell you to go ahead and stick your neck out, feel free to do something “for the good of the order,” and later “beg for forgiveness” if/when it goes south and your administrators say they do not approve. My advice: “Forget your rights” and be more aware of your image and how your actions will look to the public. Reputations are hard to restore. Being an effective teacher is all about trust and integrity, and (sorry, one more cliche) “your actions speak louder than words!”
My advice: “Forget your rights” and be more aware of your image and how your actions will look to the public. Reputations are hard to restore. Being an effective teacher is all about trust and integrity, and (sorry, one more cliche) “your actions speak louder than words!”