This is an introductory blog-post perusing my early research and resources on supporting educator health/wellness in advance to my presentation Self-Care Cookbook 2.0 – Recipes and Resources for School Leaders for the PA Department of Education’s SAS Institute 2025 state conference scheduled for December 8-10, 2025 in Hershey, PA. Here is the summary description for the workshop:

“Do you find the harried pace of our profession overwhelming and at times crushing when buried beneath decades of keeping our noses to the grindstone and putting everyone else’s needs above our own? Do some of your staff members say they are stressed out, constantly tired, plagued by one ailment after another, or wondering how they’re going to “keep up?” If health is interfering with your colleagues’ abilities to do their jobs and find success, balance, and meaning in their lives, then it is time for change. The purpose of this session is to empower school leaders and teachers with skills and attitudes needed to make informed decisions to promote self-improvements in their lifelong health and wellbeing, to LEARN tools for better time management and to help remediate fatigue, stress and burnout, CONNECT and collaborate with your staff to inspire unique strategies for better personal self-care, and ACTIVATE creative new approaches to foster an improved workplace environment.”
Actually, previous articles at this site have dived into this subject of educator stress, burnout, and the development of a health and wellness self-care plan to build resilience, work/life balance, and reignite our motivation and passion for teaching. For a complete overview, I recommend you revisit these:
- Teachers – Take Charge of Your Wellness (2025)
- Summer Reading (2021)
- Burned Out or Bummed Out? (2020)
- Teacher Self-Care During the Pandemic (2020)
- Stressed Out? (2020)
Always start with “THE WHY”
(Inspired by keynote speaker/author Simon Sinek): Why is this discussion so important now?


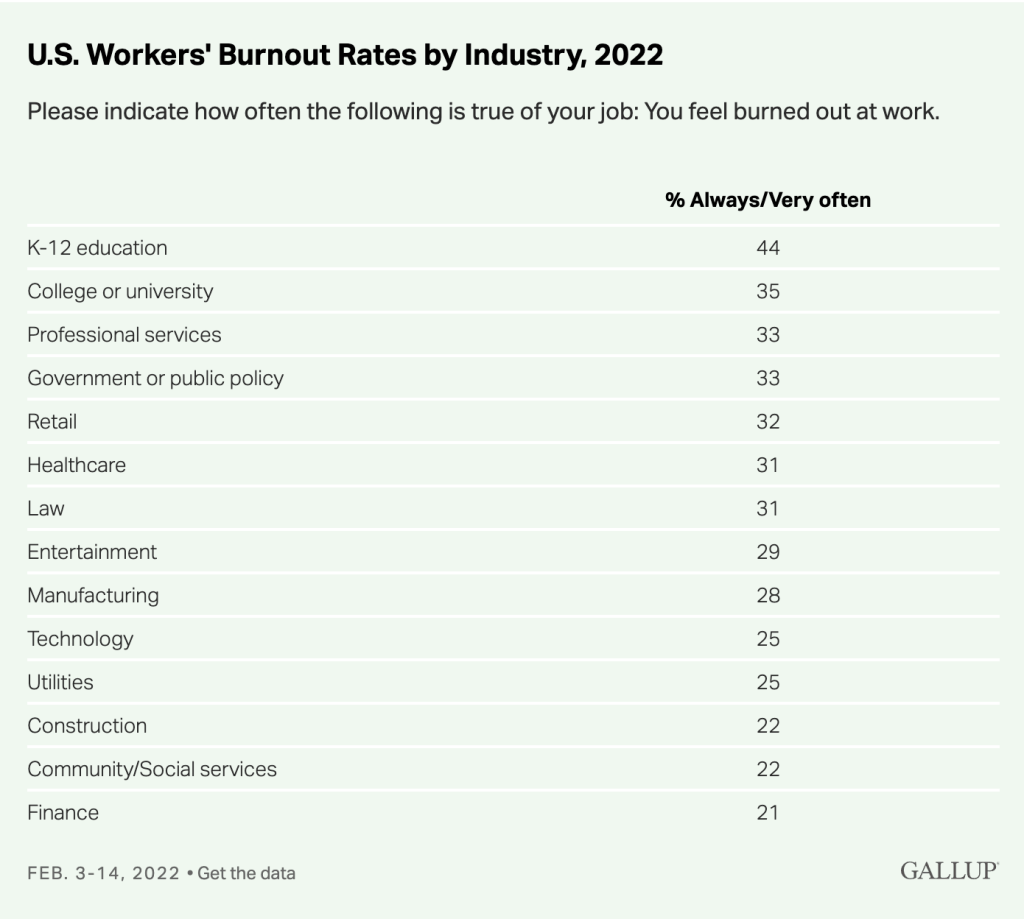
When I mentioned my research to my colleague (and former student) Dr. Timothy Wagner, Principal, Upper St. Clair High School (my former placement for full-time employment), he mentioned that this topic was timely and highly relevant, and suggested that perhaps there might be more statistics and resources “out there” on the stress of health-care workers and first-responders, which I found to be true. However, early looks have shown numerous parallels to the information in my 2023 Self-Care session.

My PDE SAS Institute session will become a “two-for-one” presentation, including the opportunity for school/system leaders, building administrators, and directors of school district professional development to also download my original “Self-Care Cookbook” (1.0) slides, recently updated for the DCMEA Annual State Conference (January 20, 2026). This self-help workshop is geared for educators to “on-their-own” explore strategies, implement use of individualized tools/remedies, and formulate new goals to improve health and wellness. Both sessions hope to cover these key questions:
- Why is it essential to personal health to achieve balance in our lives, and how can we achieve it?
- How does dedication to wellness lower the risk of illness, injury, and the quality of a person’s life?
- What are the consequences of our choices in terms of time and stress management?
- How do effective decision-making skills and goal setting influence healthier lifestyle choices?
- What are suggestions, strategies, and samples for the development of a personal self-care plan?
Using a facsimile of a prescription pad in Self-Care 1.0, I posed these personal reflections:
- How do I usually feel daily throughout the school year?
- What are the emotional and physical tolls of my job?
- What specific self-care activities do I need to incorporate to recharge and prevent burnout?
- What boundaries do I need to set around my work to honor personal time?
- What support systems can I build and/or professional help should I seek to create a sustainable practice?
Good ideas…
How can school admins support their staff in dealing with the climbing incidences of health problems, teacher exhaustion, call-offs, evidence of burnout, and high turnover rate? Sorting through a compendium of online research, these recommendations for school leaders occur repeatedly:
- Probably should go without saying: Show high visibility (“be seen by all”), recognition, and know everybody’s name. This goes a long way in building a sense of belonging of the staff and students.
- Provide more time for breaks and planning. Engage teachers in problem solving teams to identify and implement substantive ways to give them more time. Examples: cutting back on testing and data analysis; holding fewer and shorter meetings; putting a hold on new academic initiatives while increasing mental health initiatives conducted by school-based mental health professionals; hiring individuals who can assist with administrative tasks; compensating teachers for extra work; protecting classroom time by minimizing interruptions; reducing teaching hours to allow for more prep time and follow-up time.
- Foster a supportive community through mentorship programs.
- Distill high-impact strategies into a handful of manageable priorities. Once the goals are set, give teachers specific time within the school day or week to focus solely on them.
- Communicate directly, clearly, and frequently. “Supportive administrators know that a teacher’s time is valuable and that administrative meetings compete with individualized education programs, data teams, professional learning committees, cross-curricular planning meetings, and much more. So if a meeting is only for sharing straightforward information, it can be an email instead. It’s not necessary to have a meeting simply because the schedule says that faculty meetings are in the cafeteria on Mondays.” – Edutopia: “4 Practical Ways Administrators Support Teachers”
- Treat teachers with respect like the professionals they are, increasing mutual trust by decreasing micromanagement or reducing unnecessary accountability documentation.
- Shadow multiple teachers to experience first-hand the reality of their typical day.
- Allow educators the option to attend meetings and professional development activities virtually.
- Involve teachers in the creation of targeted professional development activities that are the most meaningful for them.
- Ask teachers about what specific help they need to improve classroom management.
- Develop a plan (with the Board of Education?) to increase teacher compensation over time, taking into account that many administrative and clerical tasks that are now required of teachers might ultimately be delegated to less highly compensated individuals.
- Address staff performance issues on an individual basis rather than issuing global reprimands that don’t apply to most teachers.
- Implement policies that encourage work-life balance. For example, recognize measurable indications of quality teaching rather than behaviors that signal a “more is better” approach (always coming in early and staying late, volunteering for everything, talking about working all weekend to catch up, etc.).
- Support educators by acknowledging stress, providing professional development on self-care, and creating a culture where asking for help is normalized.
- Ask teachers what mental health or other supports they need to cope with their own distress. Research has demonstrated the effectiveness of introducing trauma-informed strategies, including an emphasis on compassion fatigue and secondary trauma, as well as mindfulness strategies that are part of institutionalized wellness routines.
- Provide “safe spaces” (SEL) where educators can express themselves without fear of being judged, and practice “Mindful Leadership” to connect with and listen to them. “Getting to know your teachers on a more personal level makes it easier to identify the best thing you can do to support them, even if teachers aren’t sure what they need. The goal should be making sure everyone made it to work okay and that they’re in good spirits and ready to tackle the day.” – 7 MINDSETS: “5 Ways Administrators Can Support SEL for Teachers”
- Counteract “toxic positivity” by acknowledging that teachers are hurting and need space to grieve the continued losses associated with the pandemic.

Bad ideas…
These strategies cited by Effective School Solutions will NOT help teachers in the long-term:
- While “wear your jeans to work” days and offering coffee and donuts occasionally are nice employee appreciation efforts, they do nothing to address the underlying issues.
- Offering one-shot seminars or newsletters with suggestions about individual self-care activities (breathing exercises, physical exercise, time for self, etc.) can inadvertently place further burdens on teachers, conveying the impression that they are responsible for both creating and addressing the stress that is structural in nature.
- Don’t conduct teacher surveys or focus groups about how to reduce teacher stress and then proceed to ignore their suggestions about what would make things better.
- Don’t assume that short bursts of extra time (e.g., ending a meeting early to give teachers more time) is useful. Small, unexpected pieces of free time do not help teachers catch up with work that requires concentration and focus.
- Don’t avoid difficult conversations to address the performance problems of individual teachers by making blanket statements/warnings to all teachers, most of whom are not engaging in the problem behavior.
“Be careful not to adopt a stance of “Toxic Positivity,” that is, a stance that accentuates the positive (“we are all in this together,” “we are strong,” “it could be worse,” “look on the bright side”) while invalidating the very real pain that everyone is experiencing. Denying or ignoring unpleasant emotions tends to make them worse, not better.
– Effective School Solutions
Free Downloads
I am putting on the final touches to the SAS INSTITUTE 2025 Self-Care Cookbook 2.0 session, but have already assembled a huge bibliography of resources for your review (see below). For a “sneak preview” of my slide summary, click here. Future updates will be posted here: https://paulfox.blog/care/.
Better yet, register for the SAS Institute 2025 to see everything in person.

Sample Books
- 180 Days of Self-Care for Busy Educators by Tina H. Boogren, Solution Tree Press (2020)
- Awakened – Change Your Mindset to Transform Your Teaching by Angela Watson, Due Season Press & Educational Services (2023)
- The Balanced Band Director – Productivity and Wellness Tips to Amplify Your Impact, Not Your Workload by Lesley Moffat, Morgan James Publishing (2025)
- Demoralized – Why Teachers Leave the Profession They Love and How They Can Stay by Doris Santoro, Harvard Education Press (2018)
- Exhausted – Why Teachers Are So Tired and What They Can Do About It by Paul Murphy, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (2017)
- Fewer Things, Better by Angela Watson (2019)
- The Happy Teacher Habits by Michael Linsin, JME Publishing (2016)
- Love the Job, Lose the Stress: Successful Social and Emotional Learning in the Modern Music Classroom by Lesley Moffat (2022)
- Positive Mindset Habits for Teachers by Grace Stevens, Red Lotus 2018
- Rekindle Your Professional Fire – Powerful Habits for Becoming a More Well-Balanced Teacher by Mike Anderson, ASCD (2024)
- The Teacher’s Guide to Self-Care – Build Resilience, Avoid Burnout, and Bring a Happier and Healthier You to the Classroom by Sarah Forst, The Designer Teacher (2020)
- The Teacher’s Guide to Self-Care – The Ultimate Cheat Sheet for Thriving Through the School Year by Melanie J. Pellowski, Skyhorse Publishing (2020)
- Upbeat – Mindset, Mindfulness, and Leadership in Music Education and Beyond by Matthew Arau (GIA Publications (2022)
- The Weekend Effect: The Life-Changing Benefits of Taking Time Off and Challenging the Cult of Overwork by Katrina Onstad, HarperOne (2024)
Sample Websites
- https://7mindsets.com/5-ways-administrators-can-support-sel-for-teachers
- https://www.newleaders.org/blog/how-school-leaders-can-create-the-conditions-to-support-teacher-self-care
- https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/
- https://cea.org/burnout-is-real-98-of-teachers-better-pay-treatment-needed-now/
- https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/
- https://effectiveschoolsolutions.com/why-are-teachers-quitting/
- https://www.eschoolnews.com/sel/2023/09/22/teacher-burnout-solutions/
- https://www.edutopia.org/article/4-practical-ways-administrators-support-teachers/
- https://nafme.org/teacher-burnout-is-real-signs-and-how-to-avoid-it/
- https://www.talkspace.com/blog/self-care-for-teachers/
- https://www.edutopia.org/blog/5-tips-avoiding-teacher-burnout-mary-beth-hertz
- https://www.pbs.org/education/blogs/voices-in-education/the-3-rs-for-teacher-selfcare-reflect-release-recharge/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qPtsP7pBobI
- https://www.edweek.org/tm/articles/2014/05/20/ctq-pillars-signs-of-solutions-for-burnout.html
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/answer-sheet/wp/2014/12/12/teacher-the-day-i-knew-for-sure-i-was-burned-out/
PKF
© 2025 Paul K. Fox






































 If you are not fortunate enough to own a copy of A Field Guide to Student Teaching in Music by Ann. C. Clements and Rita Klinger (which I heartily recommend you go out and buy, beg, borrow, or steal), this blog provides a practical overview of field experiences in music education, recommendations for the preparation of all music education majors, and a bibliographic summary of additional resources. Representing that most critical application of in-depth collegiate study of music education methods, conducting, score preparation, ear-training, and personal musicianship and understanding of pedagogy on voice, piano, guitar, and band and string instruments, the student teaching experience provides the culminating everyday “nuts and bolts” of effective music education practice in PreK-12 classrooms.
If you are not fortunate enough to own a copy of A Field Guide to Student Teaching in Music by Ann. C. Clements and Rita Klinger (which I heartily recommend you go out and buy, beg, borrow, or steal), this blog provides a practical overview of field experiences in music education, recommendations for the preparation of all music education majors, and a bibliographic summary of additional resources. Representing that most critical application of in-depth collegiate study of music education methods, conducting, score preparation, ear-training, and personal musicianship and understanding of pedagogy on voice, piano, guitar, and band and string instruments, the student teaching experience provides the culminating everyday “nuts and bolts” of effective music education practice in PreK-12 classrooms. cal, and social health. They demonstrate the ability to establish and achieve personal goals. They have a positive outlook on life.”
cal, and social health. They demonstrate the ability to establish and achieve personal goals. They have a positive outlook on life.”


 Dress for success (professionally)
Dress for success (professionally)
 Pennsylvania, you should be a member of PCMEA and take advantage of the research of the
Pennsylvania, you should be a member of PCMEA and take advantage of the research of the 

 documented to a great extent, stress, burnout, and stage fright have become real concerns for music education majors completing their coursework, juries/recitals/concerts, methods exams, student teaching, and other field experiences. This may be affecting statistics on college enrollments, graduation rates, and job placements!
documented to a great extent, stress, burnout, and stage fright have become real concerns for music education majors completing their coursework, juries/recitals/concerts, methods exams, student teaching, and other field experiences. This may be affecting statistics on college enrollments, graduation rates, and job placements!
 College funding
College funding
 Music Teacher Education
Music Teacher Education 
 Learning to “manage your burdens,” class schedules, assignments, calendar, etc.
Learning to “manage your burdens,” class schedules, assignments, calendar, etc.
 2009), “deep listening” as “a way of hearing in which we are fully present with what is happening in the moment” (Barbezat and Bush 2014), contemplative movement activities including methodologies of Orff, Kodaly, Dalcroze, and Gordon adapted for other music teaching contexts (Benedict, 2010), walking meditation, tai chi ch’uan, yoga, and labyrinth walking (Center for Contemplative Mind in Society, 2016), contemplative reading, writing, and other self-help practices.
2009), “deep listening” as “a way of hearing in which we are fully present with what is happening in the moment” (Barbezat and Bush 2014), contemplative movement activities including methodologies of Orff, Kodaly, Dalcroze, and Gordon adapted for other music teaching contexts (Benedict, 2010), walking meditation, tai chi ch’uan, yoga, and labyrinth walking (Center for Contemplative Mind in Society, 2016), contemplative reading, writing, and other self-help practices.
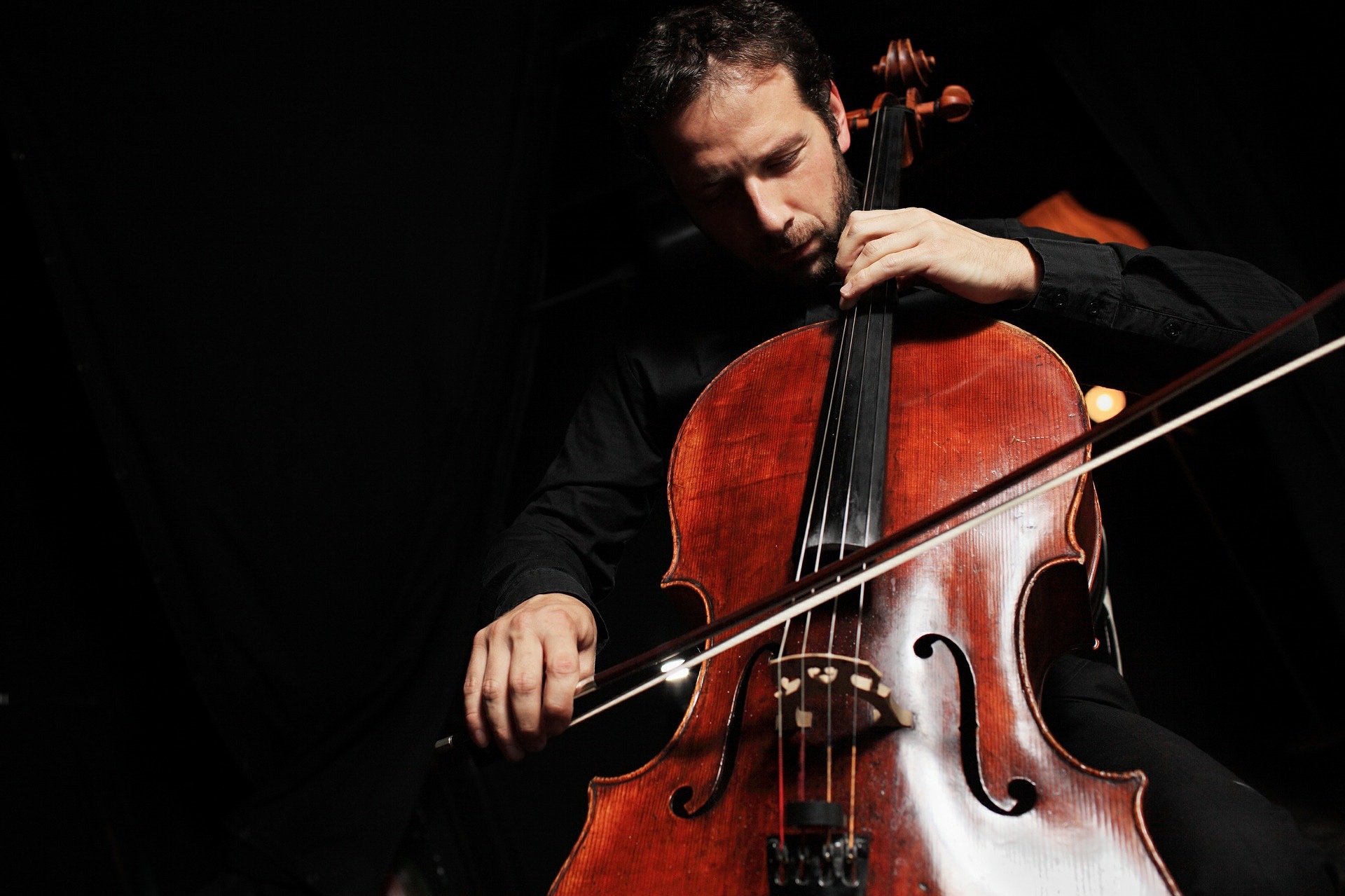



 “When musicians think about performing, they eventually think about performance anxiety — ‘stage fright.’ Performance anxiety can be defined as a physical and mental deviation from a ‘normal state’ and is perhaps one of the most misunderstood areas of performance practice… A reduction in anxiety levels especially with musicians with extensive formal training may actually diminish performance quality. For musicians with low mastery skills, the prudent approach would seem to be to undertake more formal training.” — Donald L. Hamann
“When musicians think about performing, they eventually think about performance anxiety — ‘stage fright.’ Performance anxiety can be defined as a physical and mental deviation from a ‘normal state’ and is perhaps one of the most misunderstood areas of performance practice… A reduction in anxiety levels especially with musicians with extensive formal training may actually diminish performance quality. For musicians with low mastery skills, the prudent approach would seem to be to undertake more formal training.” — Donald L. Hamann

 Job placement
Job placement

 That means, according to TIPS Retirement for Music Educators by Verne A. Wilson (MENC 1989), at least three years before you leave your full-time employment:
That means, according to TIPS Retirement for Music Educators by Verne A. Wilson (MENC 1989), at least three years before you leave your full-time employment: Robert Delamontagne writes in detail about using the
Robert Delamontagne writes in detail about using the 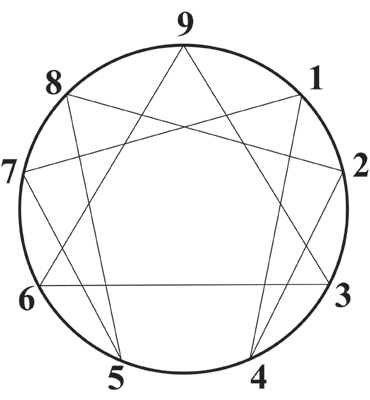 Delamontagne labels the characteristics of each E-Type. After reading his book, which ones are closest to resembling you and your spouse?
Delamontagne labels the characteristics of each E-Type. After reading his book, which ones are closest to resembling you and your spouse? On their book jacket, Duckworth and Langworthy promote their work as “a call to action on your own behalf” to:
On their book jacket, Duckworth and Langworthy promote their work as “a call to action on your own behalf” to: Life Themes Profiler, a comprehensive assessment tool developed by David Borchard and laid out initially in Chapter 4, will help you understand and graph the retirement themes and “your intentions for the next chapter of your life.”
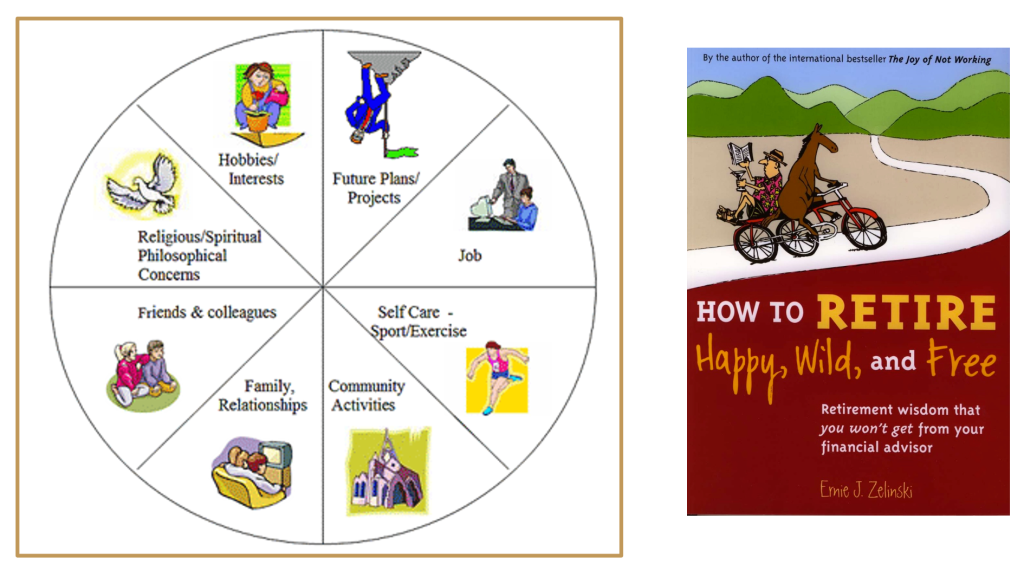
Life Themes Profiler, a comprehensive assessment tool developed by David Borchard and laid out initially in Chapter 4, will help you understand and graph the retirement themes and “your intentions for the next chapter of your life.” Obviously, fulfilling your “bucket lists” and goals will influence the structure of your daily/weekly schedule. According to Ernie Zelinski, with or without “a job,” you need to find a “work-life balance” and devote equal time to these essential priorities:
Obviously, fulfilling your “bucket lists” and goals will influence the structure of your daily/weekly schedule. According to Ernie Zelinski, with or without “a job,” you need to find a “work-life balance” and devote equal time to these essential priorities: Dave Hughes echoes these sentiments with his “four essential ingredients for a balanced life” in the book Design Your Dream Retirement: How to Envision, Plan for, and Enjoy the Best Retirement Possible (2015):
Dave Hughes echoes these sentiments with his “four essential ingredients for a balanced life” in the book Design Your Dream Retirement: How to Envision, Plan for, and Enjoy the Best Retirement Possible (2015): Do something every day that will expand your mind, stimulate your intellect, or increase your curiosity quotient.
Do something every day that will expand your mind, stimulate your intellect, or increase your curiosity quotient. Although the exact number of boomers and seniors who experience sleep problems is hard to pinpoint, a national study of our aging population suggests nearly 42 percent of those surveyed have sleep difficulties. That figure is beyond an epidemic.
Although the exact number of boomers and seniors who experience sleep problems is hard to pinpoint, a national study of our aging population suggests nearly 42 percent of those surveyed have sleep difficulties. That figure is beyond an epidemic. Regular physical activity is a must. Quoting from a future article I plan to submit to the state journal of Pennsylvania Music Educators Association PMEA News: “The definition of ‘exercise,’ especially in order to receive cardiovascular benefits, is to raise your heart rate for 30 minutes or more. Leaving your La-Z-Boy to let the dogs out or looking for the remote does not count!”
Regular physical activity is a must. Quoting from a future article I plan to submit to the state journal of Pennsylvania Music Educators Association PMEA News: “The definition of ‘exercise,’ especially in order to receive cardiovascular benefits, is to raise your heart rate for 30 minutes or more. Leaving your La-Z-Boy to let the dogs out or looking for the remote does not count!” This final category of “pre-retirement planning” has everything to do with living with independence and security as we grow older. Many Baby Boomers just starting their retirement journey may not actually see this as “a big deal” right now. However, developing a long term “backup plan” for maintaining our health care, mobility, and comfortable living is critical. Again… we must think ahead!
This final category of “pre-retirement planning” has everything to do with living with independence and security as we grow older. Many Baby Boomers just starting their retirement journey may not actually see this as “a big deal” right now. However, developing a long term “backup plan” for maintaining our health care, mobility, and comfortable living is critical. Again… we must think ahead! Fifty-five percent of our respondents wanted to stay in their own homes, with help as needed, as they got older and required more care. But a recent AARP survey revealed that only about half of older adults thought their homes could accommodate them “very well” as they age; twelve percent said “not well” or “not well at all.”
Fifty-five percent of our respondents wanted to stay in their own homes, with help as needed, as they got older and required more care. But a recent AARP survey revealed that only about half of older adults thought their homes could accommodate them “very well” as they age; twelve percent said “not well” or “not well at all.”