Leadership lessons for the classroom or staff development
This blog is a follow-up resource for my Empowering Educator and Student Leadership presentation at the PA Department of Education SAS INSTITUTE state conference on December 9, 2025 and provides a “fill-in-the-gap” narrative about many of the concepts we have already presented at this blog site:
If you would like to review my PDF slide summary from the SAS INSTITUTE, click here.
Did the main title (above) get your attention? What on earth could “leaders flush” have to do with this topic? In teaching (and modeling) leadership skills to my students, we discuss what it means to Faire sans Dire or “do without saying,” the English translation to this crest:

In other words, if you see something that needs to be done (flush the toilet?), don’t assume it’s someone else’s job. A true leader embraces the philosophy Carpe Diem (“seize the day”), identifies the problem and its solution, rolls up his/her sleeve, and “gets it done!”
Why teach leadership in the curriculum & extracurricular activities?
“Leadership is an essential skill that extends beyond the classroom, shaping how students engage with the world around them. Whether leading a group project, organizing an event, or voicing their opinions in discussions, leadership skills empower students to take initiative and make meaningful contributions. These abilities are not only beneficial during school years but also serve as the foundation for lifelong personal and professional success.”
— Bloomster
In the past, I have used a multitude of opportunities and settings to teach these life skills in summer leadership camps, section leader and student conductor seminars, drum major and marching band captain auditions, student director, producer, and musical crew head staff meetings, and for 25+ years, preparing student counselors for a comprehensive, six-day, grades 8-12 Township String Camp program.
To sum it up, teaching leadership in Grades K-12 and college settings will:
- Develop communication skills
- Build confidence & self-awareness
- Enhance problem-solving abilities
- Encourage teamwork & collaboration
- Shape future success
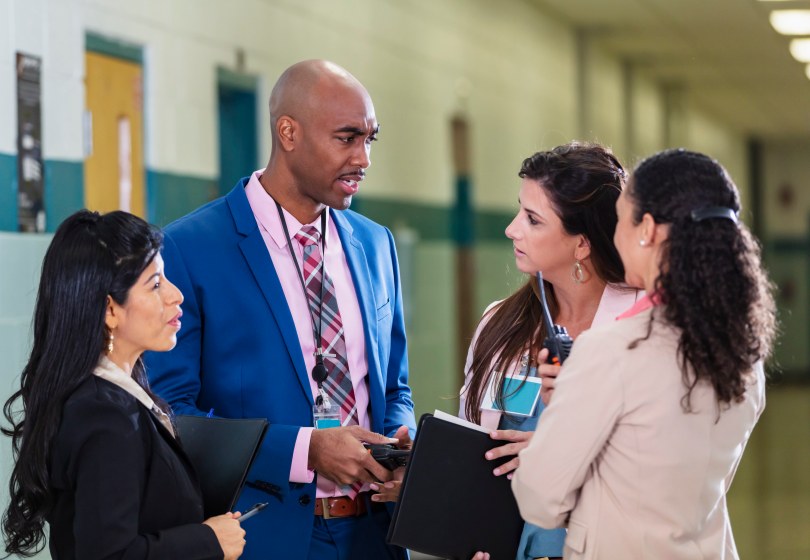
Why teach leadership to educators?
My December session at SAS Institute was geared to school/system leaders, department heads, and other administrators, but actually the focus on leadership as a skill set necessary for school/staff/individual professional improvement is essential for all educators and school support staff.
From district administrators and school principals to instructional coaches and curriculum coordinators, leaders in education have a direct impact on the learning outcomes of all students. According to UNESCO, educational leadership is considered one of the most influential factors on student outcomes, falling just behind engaging teaching. As a result, leadership training for educators has become an essential part of the professional development experience for teachers at all levels of education.
— “Building Leadership Skills – From Classroom Teacher to Educational Leader”
School improvement rarely occurs without effective leadership, and school leadership is only second to classroom teaching in its influence on student achievement. A new evidence review report from Global School Leaders paints a complex and ever-changing picture of school leaders, with their roles, responsibilities, and impact varying around the world.
— 3 Reasons Why School Leadership Is Vital to Teacher Success”

The literature suggests that empowering educators with leadership training will:
- Improve student achievement
- Empower and retain teachers
- Support new staff members
- Drive innovation and adaptability
- Bridge the gap between instruction and administration
- Build/model a positive attitude
- Enhance strategic thinking and decision-making
- Promote a positive and collaborative school climate
- Develop soft skills such as communication, conflict resolution, and building trust… both in and outside the classroom
Leadership assessments
“A leadership skills assessment is a formal evaluation used to identify and measure a person’s leadership potential and competencies, such as communication, decision-making, and emotional intelligence. These assessments can be used by organizations to evaluate current leaders, identify high-potential candidates for promotions, and inform hiring decisions. Common methods include personality tests, scenario-based assessments, and 360-degree feedback, with tools like CliftonStrengths, Hogan Assessments, and DISC being popular examples.”
— “Leadership Assessment Test – A Complete Guide 2025”
There is a large body of information out there, especially commercial resources, for evaluating the leadership quotient and achievement of corporate managers, CEOs, CFOs, etc. I was impressed with the scope and depth of the research, including these sample firms advertising the availability of third-party consultants and advisors.
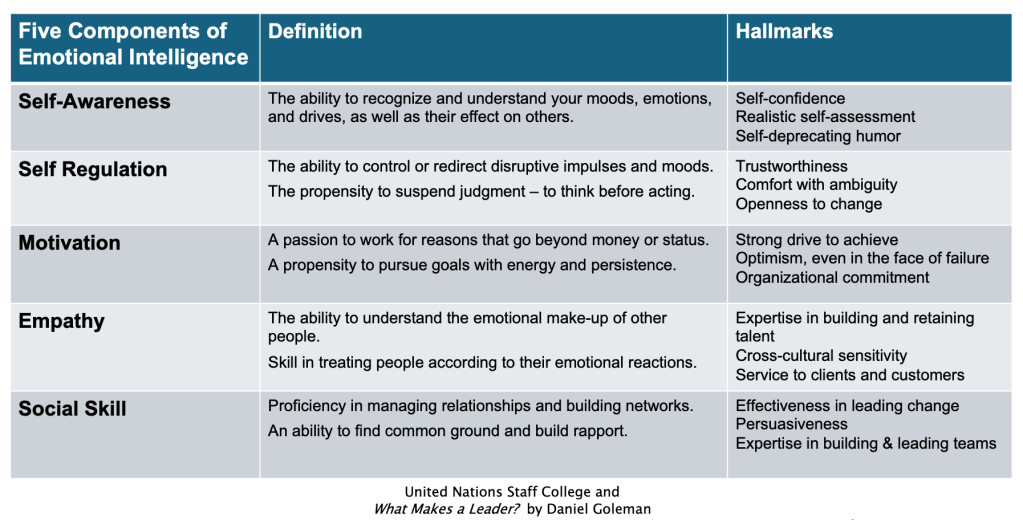
One night I randomly scanned through a handful of YouTube reels of company fraud and mismanagement (e.g., “Revenge of the Coffee Pot,” “Revenge with Karen,” and “Silent Revenge”), painting (fictitious) stories of bosses stealing intellectual property or assuming credit for the innovations/achievements of their subordinates, patent infringement, nepotism or incompetent hirings… all with arrogance, lack of professionalism, the total disregard of employee morale, and blatant patterns of poor executive decision-making, communication, emotional intelligence, strategic thinking, and the ability to influence and guide a team. “Emotional intelligence” (as defined above by Daniel Goleman in What Makes a Leader? also attributed to the United Nations Staff College) should include the “best practices” of self-awareness, self regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. Added to these YouTube (fake) scripted deficiencies are the mitigating effects of corporate politics, inconsistent application of compliance or HR policies, unclear contract language, and problems in the chain of command… with the eventual result of the boss receiving a fall from grace, termination, and other legal consequences. Most of these episodes imply only the Board of Directors evaluates the top executives (like school superintendents?), and even with the inclusion of employee satisfaction surveys, staff retention data, third-party auditors, and whistle-blower protections in some instances, the catastrophic actions of these leaders nearly destroy the businesses. For these videos, it seems that leadership assessments and goals are never ongoing, the benchmarks are seldom reviewed, and nothing is PROACTIVE… and therefore not preventive. Therefore, for the school district and corporate worlds alike, we need to intentionally provide formative assessments of our leaders (and ourselves). Exactly what do we need to know and do to improve?
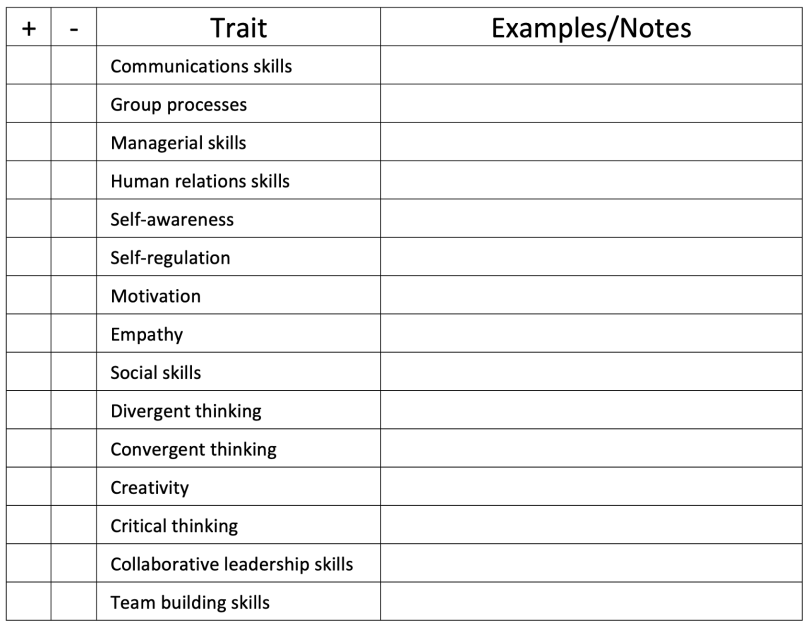
In my blog Growing Student Leaders and the SAS Institute 2025 presentation, I offered the above image as an informal personal checklist to evaluate leadership traits. Coincidentally, while I was writing this article, a scholarship committee of the Community Foundation of Upper St. Clair (for which I serve as Communications Director and Arts Chair) was developing an assessment rubric for ranking applications of a new student leadership scholarship. Although still under development, here are a few of the categories being considered:
- Communication: Includes listening skills, clarity in speaking, and the ability to make others feel heard.
- Integrity: Acting ethically, being trustworthy, and aligning actions with words.
- Accountability: Taking ownership of actions and commitments.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with others, valuing different perspectives, and resolving conflicts.
- Self-awareness: Understanding one’s own strengths, weaknesses, and biases.
- Drive/Initiative: A bias for action and the ability to move projects forward.
- Courage: The bravery to speak truthfully, admit shortcomings, and make difficult decisions.
- Humility: Recognizing the contributions of others and remaining a lifelong learner.
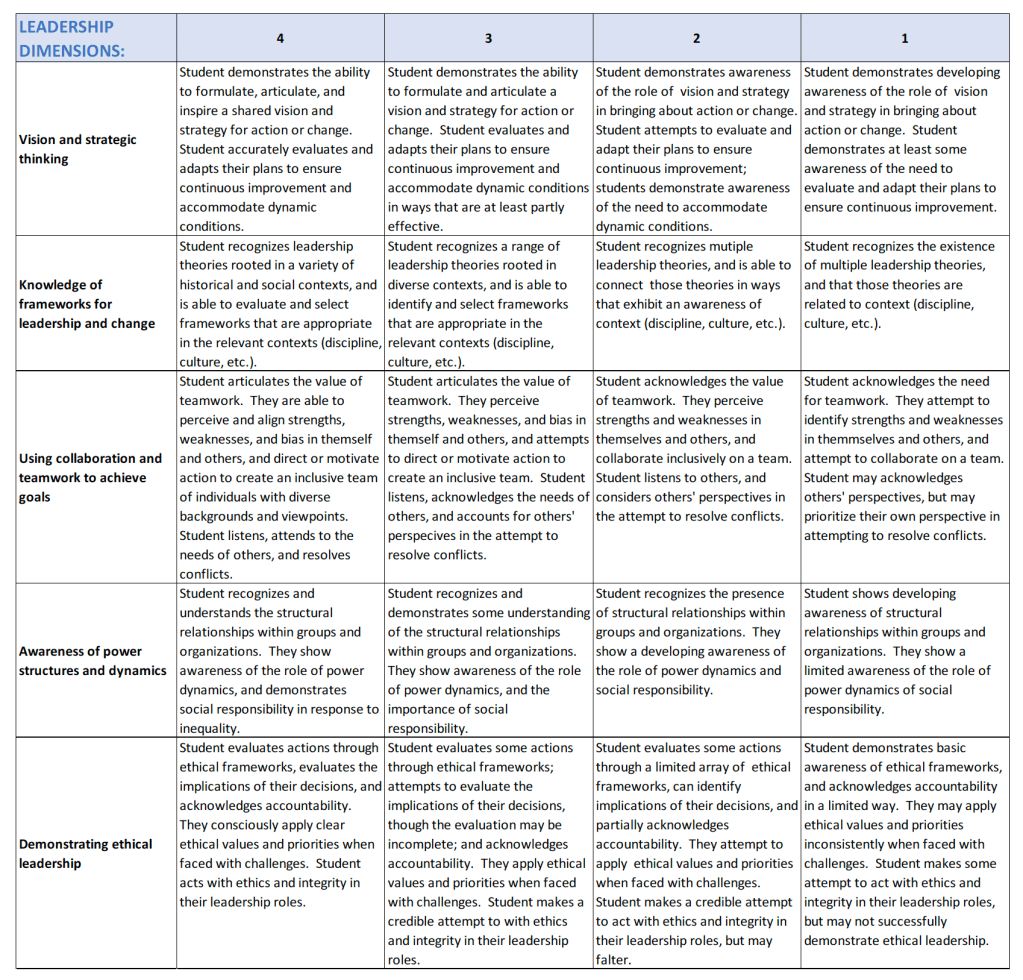
The University of Massachusetts Lowell developed the above rubric for their River Hawk Experience Distinction Leadership Program, defining specific criteria with a clear description of what each trait should look like at different performance levels, in order to provide a standardized way of measuring and assessing leadership skills

In addition, the National Education Association has created the above NEA Leadership Competency Guide worth downloading.
My favorite inspirational speaker Simon Sinek has also weighed in on this topic of “What Makes a Great Leader?” refining/simplifying it to just three traits:
- Courage
- Integrity
- Communication

Additional resources
If you are an educator looking for supplemental material on developing leadership skills in your students, besides these SAS INSTITUTE 2025 slides (of which the original PowerPoint file is available to download for free in order to adapt for your classroom – please email me), I recommend perusing the full-blown “Building Leaders for Life” (second edition) curriculum (94 lessons in five subject areas, 355 pages of lesson materials, 137 student handouts) created by the Association of Washington Student Leaders (a division of the Washington School Principals’ Education Foundation). Click here to view their website. They also have a middle school and elementary series!
If you attend my SAS INSTITUTE workshop on December 9, 2025 (starting at 9:40 a.m. in Magnolia C, Hershey Lodge & Convention Center), ask me to see sample materials from their high school course of study.
Finally, here is the “homework for future leaders” I provided at the SAS INSTITUTE and during a 2024 summer camp at Upper St. Clair High School, providing additional links to many inspiring minds. Enjoy!
Leadership is not about being in charge. It is about taking care of those in your charge. — Simon Sinek
A leader is one who knows the way, goes the way, and shows the way. — John C. Maxwell
Do not follow where the path may lead. Go instead where there is no path and leave a trail.
— Ralph Waldo EmersonThe greatest leader is not necessarily the one who does the greatest things. He is the one who gets people to do the greatest things. — Ronald Reagan
What you do has far greater impact than what you say. — Stephen Covey
PKF
© 2025 Paul K. Fox

















 His latest book, Leaders Eat Last, brings up the rationale of mutual collaboration and prioritizing the mission and the needs of your team members. Sinek observed that some teams were able to trust each other 100%, so much so that they would be willing to put their lives on the line for each other, while other groups, no matter what enticements or special incentives were offered, were “doomed to infighting, fragmentation and failure.” Why was this true?
His latest book, Leaders Eat Last, brings up the rationale of mutual collaboration and prioritizing the mission and the needs of your team members. Sinek observed that some teams were able to trust each other 100%, so much so that they would be willing to put their lives on the line for each other, while other groups, no matter what enticements or special incentives were offered, were “doomed to infighting, fragmentation and failure.” Why was this true? Also intriguing is an expanded Chapter 24 and Appendix section in the book called “A Practical Guide to Leading Millennials.” Similar to another suggestion for summer perusal, UnSelfie: Why Empathetic Kids Succeed in Our All-About-Me World by Michele Borba, Ed.D (Simon & Schuster, 2017) which focuses more on our current young “charges,” Sinek’s differentiation is provided to inspire and educate the ultimate multitaskers of the “distracted generation.”
Also intriguing is an expanded Chapter 24 and Appendix section in the book called “A Practical Guide to Leading Millennials.” Similar to another suggestion for summer perusal, UnSelfie: Why Empathetic Kids Succeed in Our All-About-Me World by Michele Borba, Ed.D (Simon & Schuster, 2017) which focuses more on our current young “charges,” Sinek’s differentiation is provided to inspire and educate the ultimate multitaskers of the “distracted generation.”
![US Navy SEAL Team Three [ST3][Patch][1.5]](https://paulfox.blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/us-navy-seal-team-three-st3patch1.5.png) No Bad Teams, Only Bad Leaders
No Bad Teams, Only Bad Leaders

 One Minute Manager by Ken Blanchard and Spencer Johnson
One Minute Manager by Ken Blanchard and Spencer Johnson



 No teacher will have any patience listening to your whining or remarks of “could have,” “would have,” or “should have been” excuses. What have we always wished for? “If only I had enough time to learn that new scale, étude, or song!” “With all of my other academic assignments, sports events, and extracurricular activities, how can I fit in moments for listening to bands, orchestras, or classical virtuoso artists performing on the web?” “When am I ever going to have the chance to compose…” (or “arrange” or “record” or “memorize” or “conduct” or “choreograph”) “…that piece?” “When will I get around to learn this new technique, practice sight-reading, or dive into those drills designed to improve my key literacy, rhythmic precision, tone, intonation, range, form, coordination, embouchure, stick rudiments, or bow control?
No teacher will have any patience listening to your whining or remarks of “could have,” “would have,” or “should have been” excuses. What have we always wished for? “If only I had enough time to learn that new scale, étude, or song!” “With all of my other academic assignments, sports events, and extracurricular activities, how can I fit in moments for listening to bands, orchestras, or classical virtuoso artists performing on the web?” “When am I ever going to have the chance to compose…” (or “arrange” or “record” or “memorize” or “conduct” or “choreograph”) “…that piece?” “When will I get around to learn this new technique, practice sight-reading, or dive into those drills designed to improve my key literacy, rhythmic precision, tone, intonation, range, form, coordination, embouchure, stick rudiments, or bow control?
 The mission of South Hills Junior Orchestra, which rehearses and performs at the Upper St. Clair High School in Pittsburgh, PA, is to support and nurture local school band and orchestra programs, to develop knowledge, understanding, performance skills, and an appreciation of music, to increase an individual member’s self-esteem and self-motivation, and to continue to advance a life-long study of music. Members of the Orchestra learn, grow, and achieve positions of leadership to serve their fellow players.
The mission of South Hills Junior Orchestra, which rehearses and performs at the Upper St. Clair High School in Pittsburgh, PA, is to support and nurture local school band and orchestra programs, to develop knowledge, understanding, performance skills, and an appreciation of music, to increase an individual member’s self-esteem and self-motivation, and to continue to advance a life-long study of music. Members of the Orchestra learn, grow, and achieve positions of leadership to serve their fellow players.