
Before you begin reading this article, please take a moment and peruse these past blog posts:
Although several of the cited research links may have expired (for example, PA Department of Education modified most of their website’s URLs), these provided the foundations of background information and references for the presentation I prepared for the DCMEA Virtual Conference in 2020 (during COVID) and serve as the starting point for the workshop I will share in-person at the DCMEA Winter Conference in January 2026. This blog provides updates and additional perspectives. Taken in combination with the above sources, you will be able to identify the benefits, positive models, precautions, and dangers of social media, social networks, professional learning networks, and sample emerging technologies as they apply to teachers’ professional development and education of students.
“THE WHY”
Before every clinic or publication I develop, I always try to spotlight the theme of “THE WHY” as preached by one of my favorite authors and motivational speakers – Simon Sinek! According to him, for organizations and individuals alike, “THE WHY” (rationale and priority) is more important than “THE WHAT” and “THE HOW.” (See this video.)
WHY is a collaborative discussion on social media essential? Why now?
”There’s a growing body of evidence suggesting that educators are facing increasing scrutiny regarding their social media use. Concerns include unprofessional conduct, inappropriate interactions with students, and the potential for cyberbullying and other negative impacts on student well-being.”
“Educators are increasingly concerned about how social media influences students’ social-emotional development and their interactions with others.”
— NEA Member Polling on Social Media…
— NEA Impact on Social Media and Personal Devices on Mental Health
— HHS Youth Mental Health and Social Media
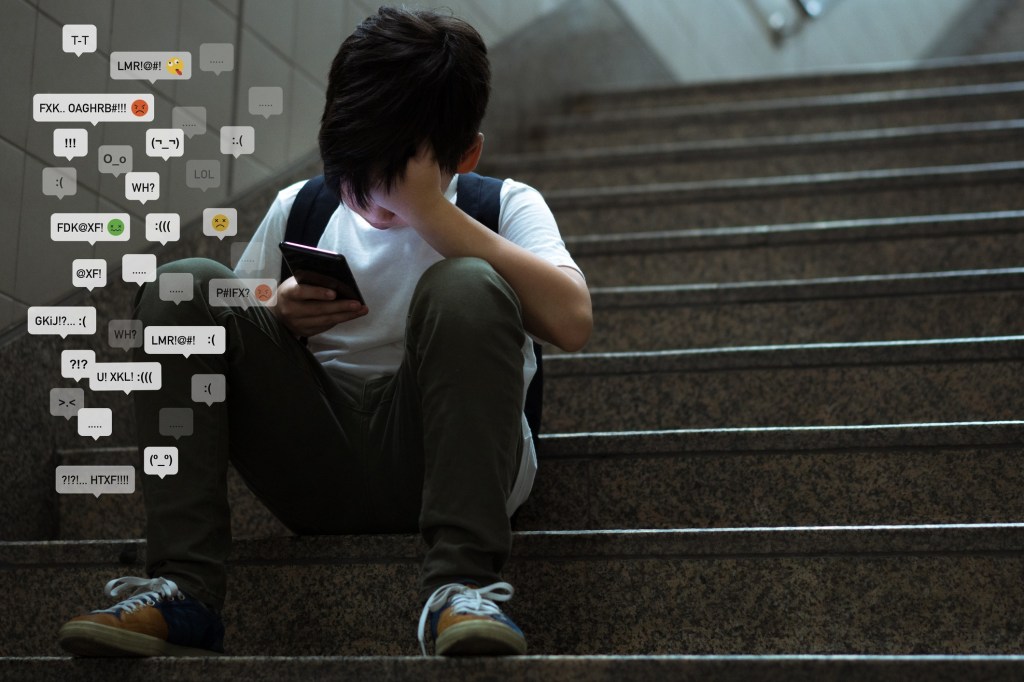
Frankly, there is still a lot of confusion about the dangers of social media, social networking, and other technology integrations into education. In Social Media – Boon or Nemesis, we mentioned that teachers should “debunk the free speech myth.” We demonstrated how the improper application of social media could get educators in trouble. Check out these sites for more info and corroborative stats:
— Teacher Student Misconduct and the Critical Role of Social Media Screening
— NCBA Social Media for School Employees
— Social Media Hazards and Tips for Teachers

As always, our goal is to promote ethical practices in maintaining professionalism in the digital world.
“THE WHAT” — Review of Definitions
“Social Media”
Social media are “websites and applications that enable users to create and share content or to participate in social networking.”
— Oxford Lexico.com online dictionary
“Social Network”
A social network is, 1. a network of social interactions and personal relationships.; 2. a dedicated website or other application which enables users to communicate with each other by posting information, comments, messages, images, etc.
— Oxford Lexico.com online dictionary
“Professional Learning Community” (PLC)
A PLC is “a group of educators who meet regularly…” (usually in-person) “…to strategically enhance their teaching skills and improve student outcomes.”
versus “Professional Learning Network” (PLN)
A PLN is “a group of educators who gather more informally…” (usually in online communications) “…to problem-solve and generate ideas to enhance classroom practices. A PLN… often takes the form of an open forum, where participants can ask and answer questions based on their experiences.”
— https://edtechmagazine.com/k12/article/2024/08/pln-vs-plc-perfcon
“THE HOW” — Ethos of Care

Teachers use social media to…
- Get inspired with new teaching ideas
- Find resources for the classroom
- Connect with other educators
- Stay on top of trends and news
- participate in an online community
- Find teacher discounts and deals
- Follow education companies and organizations
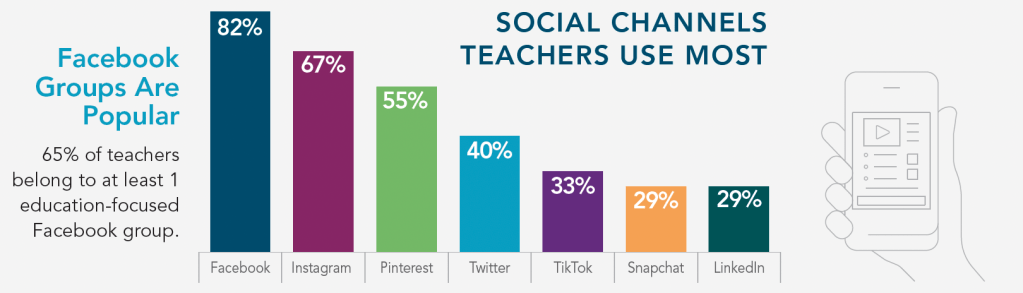
— How Teachers Use Social Media
— Teachers Social Media Use

— Social Networks for Teachers
We acknowledge that the benefits of social networking for educators are numerous by promoting professional collaboration and connections, including:
- Acquiring information to enhance understanding
- Keeping informed about latest developments in education
- Enhancing communications with students, parents, and the school community
- Fostering connections with colleagues in the field to expand an educator’s professional network.
— Benefits of Social Media as an Educator

However, educators must exercise “sound judgment” and proper professional boundaries when using social media/networks with students. While the introduction of new technology provides many opportunities for teaching and learning, it is important to establish clear rules for appropriate student-teacher communication. In order to promote safety and appropriate boundaries while transitioning to a virtual teaching and learning environment, the Pennsylvania Professional Standards and Practices Commission offers suggestions to help educators protect themselves and their students.
- All technological resources and applications should be school entity-approved and only used in the manner prescribed. Ensure that you are familiar with the tools you are using in order to use them properly.
- Communication with students should occur at designated times, consistent with traditional school day hours. Maintain transparency and protect yourself by keeping a record of all communications with students.
- Clearly communicate when and how students should contact you and provide a timeframe for when students should expect responses to questions.
- Avoid one-to-one interactions with students in chatrooms, FaceTime, Skype, or any other online space. School psychologists, school counselors and others providing one-to-one services to students should consult with school administration about the best mode of communication.
- Use approved forms of communication by your school entity to connect with students and parents (i.e. Remind), use only your school email to communicate, and copy administration when communicating with parents or students.
- When creating content or interacting in an online space with students, conduct yourself as you would if you were in school. If appearing on camera, dress professionally and be mindful of your surroundings and the camera’s view.
- Do not “friend” or follow students on social media and do not allow students to “friend” or follow you on your personal social media. Remember, you do not have a “social” relationship with your students.
- Keep your personal and professional lives separate. Do not share overly personal information about yourself with students.
— PSPC Digital Tips for Educators

While exercising responsibility to maintain a respectful, safe, online environment, there are many benefits for the application of social media for students in the classroom:
- Real-time communications can increase student engagement, collaboration, communication and overall participation
- Many students may find it easier to participate in online discussions that in the classroom
- Students can easily ask each other or their teacher questions about assignments outside of class
- Students & teachers can quickly share resources at any time.
- Teachers can easily share class announcements.
- Social media can provide a contingency plan for last minute remote learning scenarios.
- Students can organize school events with each other or with the help of a teacher.
- Teachers can augment an online-only class by establishing a social media page or account simply for building community.
- Students can practice using social platforms responsibly, including maintaining a respectful online discourse.
- Teachers can communicate directly with parents as needed, and parents can stay informed of school news via a convenient, easily accessible platform.
However, please watch out for these potential drawbacks:
- Social media can be a major distraction, especially if students are accessing their personal accounts independently.
- If students primarily use social platforms to participate in class discussions, they can miss out on practicing face-to-face conversations and respectful in-person discourse.
- Some students may see social media assignments as an opportunity to cyberbully their classmates, and there is always a risk of someone posting inappropriate content or language.
“THE WHAT” — Several Success Stories
Balancing the positives and negatives and taking into account all of these precautions in order to maintaining professional boundaries, the integration of new technology into the classroom may offer excellent enrichment and increase student motivation for advanced learning. This may take many forms. Here are a few interesting models.

Prior to preparing for the DCMEA online session in 2020, I stumbled upon a truly inspiring post from Derek Muller, a gifted teacher, physicist, filmmaker, and founder of the YouTube channel Vertiasium which has captured millions of subscribers. He offers one of the BEST models of using social media to enrich the understanding of learning math and science (applicable to all fields of study), while at the same time, provides warnings against unbridled use of so-called “innovation for innovation’s sake.”
“I feel like people over the years are invariably drawn to use these words: revolutionize and education. And there’s this sort of amnesia that we’ve had a hundred years’ worth of these predictions, worth of really groundbreaking technologies that have transformed other areas in our lives but have failed to fundamentally change the way we do education. So, I stand here today as a voice of caution, to think that the future of education is not one of revolutions…”

You need to watch this: How is Social Media Transforming the Future of Education? (2016)
— Derek Muller
Say what you want about how COVID significantly disrupted our educational programs, evidence of learning loss, problems in socio-emotional development, decline of student engagement and self-motivation, rise in mental health struggles, decreased instructional time, and the effects of a new digital divide of under-served students (Annie E. Casey Foundation), happily there were surprisingly a few positive advancements — the results of exploring new tools and methodologies we had to employ to tread water and cope with the catastrophe. (“When life hands you lemons, make lemonade!”)

As one example, in the middle of preparing music for my community orchestra, we were shut down in 2020. No in-person rehearsals at the school. I then pivoted to creating my own online platform called SHJOOLA (South Hills Junior Orchestra Online Academy) in 2021 using MusicFirst. For a nominal yearly subscription fee, I was able to continue my Saturday morning classes (synchronous) as well as asynchronous (on-their-own time) learning using excellent applications in a virtual environment: MusicFirst Classroom, Focus on Sound, PracticeFirst, Sight-Reading Factory, Musition, Auralia, a web-based music notation program, and a huge library of method books and ensemble music. Several past blogs showed how we rolled out SHJOOLA:
The latter link above also provided a comprehensive list of supplementary resources (at the time) for online music education. Please peruse these even though some of them may have now gone inactive. We will provide supplemental links at the bottom of this article.
Another direction accented by the onslaught of the pandemic was digital streaming performances, incorporating technology in both the solo and ensemble settings. The following are two of my favorite examples of these to be viewed on YouTube:
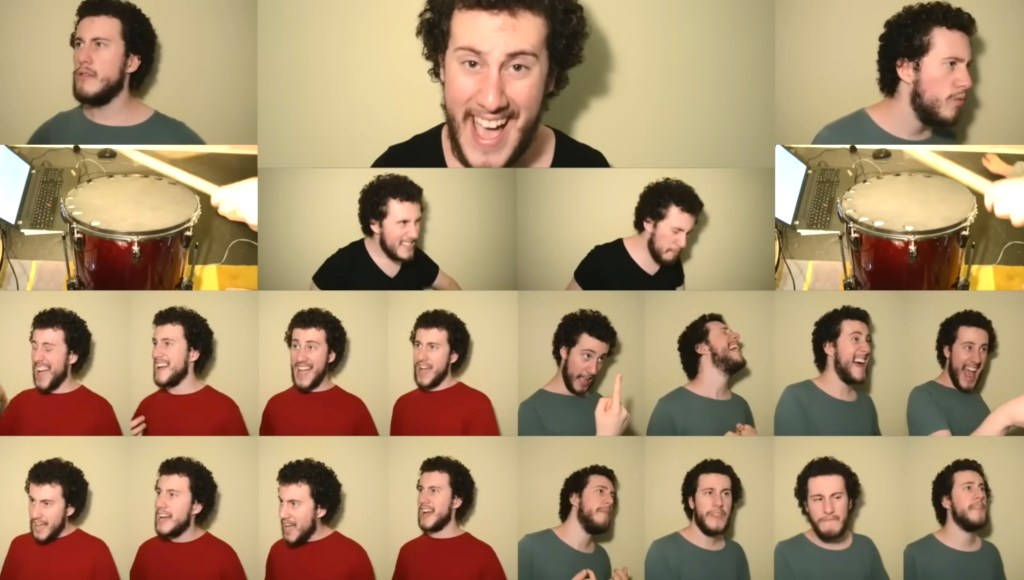

Circle of Life from Disney’s Lion King (2015-18) by Sam Robson, arranger, innovator and performer using multitrack recording of a single performer mixing as many as 50 voices at one time.

Cloudburst, a Virtual & Live Choir and TEDTALK (2013) by Eric Whitacre
Well… sorry this blog has grown to be so large! If you admit to understanding the potential hazards of and precautions for integrating social media, social networks and other technologies into education, we’ll close with the following bibliography of additional resources for further study. If that is not enough to whet your curiosity, stop back in several months to download a copy of my slide summary for the session I will present at the DCMEA Winter Conference on January 30, 2026.
Be careful — stay safe and professional — but ENJOY!

Sample Blogs
- How Music Teachers Can Use the Power of Social Media by Amanda Green (SocialMediaToday)
- Ms. Aileen ’s Music Room “Social Media for Music Teachers” by Aileen Miracle
- Social Media Apps and the Music Classroom by Paulo Camacho
- Social Media for Teachers by Matt Davis
- Harnessing Social Media for Music Education by Denise Vasenin & Jose Valentino Ruiz
Several Major Platforms
Examples of Music Applications/Websites
- http://www.gmajormusictheory.org/
- http://www.musictheory.net/
- http://www.good-ear.com/
- https://my musictheory.com/music-theory-quizzes/
- http://www.davesmey.com/index.htm
- http://www.teoria.com/
- http://www.ars-nova.com/theory.html
PKF
© 2025 Paul K. Fox



 you to reflect and respond to “what would you do?” and even re-orient you to the paradoxes in which you may encounter that may not seem to offer an obvious resolution.
you to reflect and respond to “what would you do?” and even re-orient you to the paradoxes in which you may encounter that may not seem to offer an obvious resolution. Use of social media networks to support student learning versus the risk of crossing the student/teacher boundary with inappropriate informal communications? (See
Use of social media networks to support student learning versus the risk of crossing the student/teacher boundary with inappropriate informal communications? (See  To foster meaningful scrutiny and study of the bulleted issues in bold above, we will sort these problems by Principle III “Responsibility to Students” and Principle IV “Responsibility to the School Community” of the National Association of State Directors of Teacher Education and Certification (NASDTEC) “Model Code of Ethics for Educators” (MCEE):
To foster meaningful scrutiny and study of the bulleted issues in bold above, we will sort these problems by Principle III “Responsibility to Students” and Principle IV “Responsibility to the School Community” of the National Association of State Directors of Teacher Education and Certification (NASDTEC) “Model Code of Ethics for Educators” (MCEE): 



 MY SOLUTION: This is more common than you would like. This episode compels you to figure out how to wear two unique hats simultaneously – the educator and the judge. Assuming you were clear (in writing) on the requirements of the try-outs, even sharing the blank rubric that would be used for the evaluations, you are now charged to find the “best” person for each lead assignment based on a number of criteria:
MY SOLUTION: This is more common than you would like. This episode compels you to figure out how to wear two unique hats simultaneously – the educator and the judge. Assuming you were clear (in writing) on the requirements of the try-outs, even sharing the blank rubric that would be used for the evaluations, you are now charged to find the “best” person for each lead assignment based on a number of criteria:
 Workplace” are applicable
Workplace” are applicable 