The Five C’s of Self-Care
What profession has the highest rates of stress and burnout?
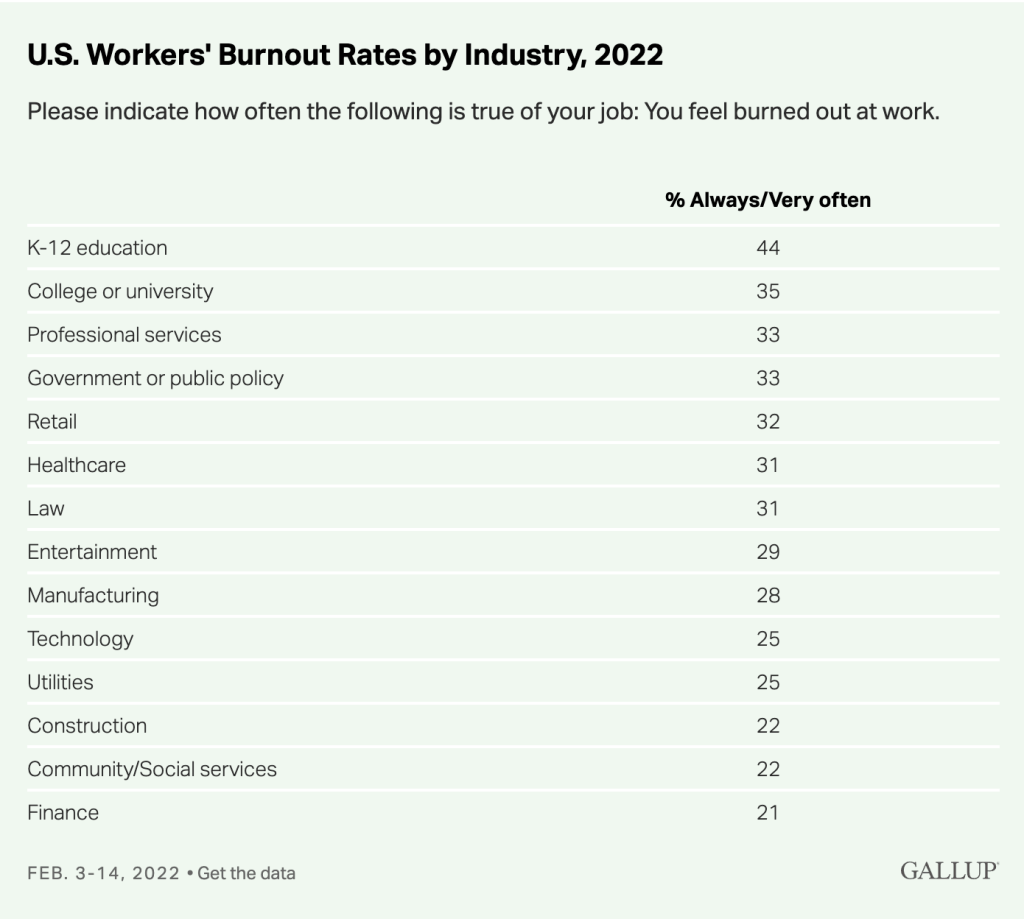
The answer is… educators of grades K to 12. NO FOOLIN’ ⏤ yes, even though today is April Fool’s Day!
The Crisis
Citing a 2022 Gallup Poll at Purdue Global’s website here, “K-12 teachers are the most burned out profession in the U.S.” They go on to say:
In fact, teachers have higher-than-average stress levels compared to other client-facing professionals. This kind of stress can lead to physical and mental health concerns for teachers and negatively affect students’ well-being and achievement.
“Being an educator requires so much of us,” says Carol Laman, faculty member at Purdue Global. “It is emotionally, physically, and mentally demanding.”
Self-care practices can help. According to the National Comprehensive Center, self-care can aid educators in both improving their overall wellness and being more effective for their students. ⏤ https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/
According to the National Education Association, we have a MAJOR problem!
A study by the advocacy group, Alliance for Excellent Education, reports that 40-50% of new teachers leave within their first five years on the job. Many factors contribute to the high dropout rate, a severe lack of work-life balance and the inevitable high stress levels teachers feel on the job, to name a few. Because of this, self-care is extremely important for teachers. However, it’s hard for teachers to take care of themselves when their career is taking care of students. ⏤ https://www.nea.org/professional-excellence/student-engagement/tools-tips/importance-self-care-teacher
This statistics are overwhelming, as documented in the Teacher Wellbeing Survey by Panorama Education.
Teacher wellness has a significant impact on school climate and student learning. Yet teacher stress and burnout continue to present retention and turnover challenges in districts: 85 percent of teachers have reported that work-life imbalance affects their ability to teach. More than one in five new teachers leave the profession within their first five years of teaching—and this attrition is substantially worse in high-poverty schools. ⏤ https://www.panoramaed.com/products/surveys/teacher-well-being-survey

The Concern – What is “Self-Care?”
The online Oxford dictionary defines “self-care” as “the practice of taking action to preserve or improve one’s own health,” or “the practice of taking an active role in protecting one’s own well-being and happiness, in particular during periods of stress.”
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) provides even more clarification:
Self-care means taking the time to do things that help you live well and improve both your physical health and mental health. This can help you manage stress, lower your risk of illness, and increase your energy. Even small acts of self-care in your daily life can have a big impact.
⏤ https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/caring-for-your-mental-health.
The National Wellness Institute (NWI) further defines wellness as a “conscious, self-directed, and evolving process of achieving one’s full potential… [It] is positive, affirming, and contributes to living a long and healthy life.” NWI addresses six dimensions of wellness, the combination of which “enables us to thrive amidst [life’s] challenges.”
- Emotional
- Physical
- Intellectual
- Occupational
- Spiritual
- Social
In our profession, the defining concerns also involve other major “C’s” within the school workplace – climate and culture – and that “actions speak louder than words!” Edutopia dove into this topic in their blog, “Leaders Must Address Teacher Well-Being With Action, Not Just Self-Care Talk” here.
By listening to educators and building supports that reflect their genuine needs and concerns, these leaders are shifting school cultures in ways that go beyond lip service.
⏤ https://www.edutopia.org/article/leaders-teacher-wellbeing-action

The Causes
That leads us to THE WHY – why is this such a crisis?
In my educator self-care workshops (e.g., this example), I bring up the research of Paul Murphy from his book Exhausted – Why Teachers Are So Tired and What They Can Do About It. Consider his litany of possible culprits that may cause burnout in some teachers:
- Lack of autonomy
- Dysfunctional work environment
- Inadequate social support
- Extremes of activity
- Poor work/life balance
Another excellent read on the subject is Demoralized – Why Teachers Leave the Profession They Love and How They Can Stay. Author Doris Santoro takes a closer look at these issues:
- Teachers feel frustrated from accomplishing good work that benefits students, communities, and the profession.
- Problem is external and does not indicate a “weakness” or lie within the individual teachers themselves.
- Dissatisfaction in education is due to moral and ethical conflicts.
Only by addressing the moral sources of teacher’s anguish might we stem the tide of teacher exodus. ⏤ “The Problem with Stories About Teacher Burnout” by Doris Santoro in Kappan December 2019/January 2020
What are the symptoms of “burnout?” From the Mayo Clinic and other sources, we learn the following. Do you display any of these on a regular basis?
- Disillusionment over the job
- Cynicism at work
- Impatience with co-workers, administrators, and students
- Lack of satisfaction in accomplishments
- Dragging themselves to work and trouble getting started once they’re there
- Lack of energy
- Unexplained aches/pains
- Self-medicating with food, drugs, or alcohol
- Changes in sleep/eating patterns
Are these striking close to home? If you said, “Yes, that’s me!” more than a couple times, it is time to seek help. Please consider this a “wake-up call” to visit your health care professional.

The Courses-of-Action
If you Google search “teacher self-care” in your browser, the following comes up from the (experimental?) Google-generative AI Overview, otherwise a good starting point summarizing possible solutions for stress remediation and improving over teacher mental health.
Key Self-Care Strategies for Teachers
- Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as it’s a cornerstone of self-care and impacts teaching performance. https://www.kirstenskaboodle.com/what-are-the-benefits-of-sleeping-for-educators and https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/heres-how-you-can-enhance-your-productivity-efficiency-psevc
- Engage in Physical Activity: Regular exercise releases endorphins, reducing stress and improving mood. https://proactiveapproaches.co.uk/promoting-self-care-for-teachers-supporting-wellbeing-in-trauma-informed-classrooms
- Practice Mindfulness and Meditation: Incorporate mindfulness techniques or meditation to reduce stress and cultivate present-moment awareness. https://insighttimer.com/meditation-courses/course_danielle-nuhfer-path-of-the-mindful-teacher and https://www.brilliantmindfulness.com/mindfulness-programs-for-teachers/
- Foster Social Support: Connect with friends, family, or colleagues to build a strong support network. https://www.unicef.org/learning-crisis/self-care-tips-for-teachers and https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/what-practical-ways-prioritize-teacher-self-care-bs32e
- Set Boundaries: Establish clear limits on work hours and responsibilities to maintain a healthy work-life balance. https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/what-practical-ways-prioritize-teacher-self-care-bs32e
- Engage in Hobbies and Relaxing Activities: Make time for activities that bring you joy and help you recharge. https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/ and https://www.unicef.org/learning-crisis/self-care-tips-for-teachers
- Reflect on Your Practice: Regularly reflect on your teaching experiences, identifying both challenges and successes. https://reflectiveteacher.cloud/2024/01/19/power-of-reflective-teaching-strategies-for-classroom-practice
- Seek Professional Counseling: Don’t hesitate to seek professional support if you’re struggling with stress, burnout, or other challenges. https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/ and https://www.unicef.org/learning-crisis/self-care-tips-for-teachers
- Eat Well: Nourish your body with healthy meals and snacks to maintain energy and focus. https://www.unicef.org/learning-crisis/self-care-tips-for-teachers
- Take Breaks: Schedule regular breaks throughout the day to decompress and avoid feeling overwhelmed. https://www.justaddiceorchids.com/orchid-care-blog/self-care-for-teachers
- Create a Routine: Establish routines for both home and school to provide structure and stability. https://new.academy4sc.org/2025/03/19/teaching-about-self-care and https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps to avoid feeling overwhelmed. https://avidopenaccess.org/resource/r-you-ready-to-recharge-tips-for-teacher-self-care/
- Be Kind to Yourself: Practice self-compassion and acknowledge your efforts and achievements. https://educators4sc.org/teaching-about-self-care/ and https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10643-022-01432-0
- Connect with Loved Ones: Plan to connect with family and/or friends every day. https://kognito.com/blog/combating-teacher-burnout-self-care-strategies-for-educators/
Paul Murphy added these “remedies” for improving teacher time management, promoting better work/personal life balance, and de-stressing:
- Work less/fewer hours
- Realize that time before school is worth more than twice as much as time after school (so plan accordingly)
- Use class time to check work
- Leverage technology
- Don’t grade everything
- Stop assigning things

The Courage to Change!
The bottom line – We are our own worst enemies!
Our negative thoughts, self-doubt, and destructive behaviors often hinder our own progress and happiness, making us our own biggest obstacles. ⏤ Google Generative AI and other sources including https://lorimilner.medium.com/the-art-of-being-your-own-worst-enemy-c393e9032d27, https://markmanson.net/when-you-are-your-own-worst-enemy, and https://letherspeakusa.org/why-are-we-our-own-worst-enemies/.
The research suggests that many “bad habits” may disrupt our ability to take care of ourselves and seek change, such as these:
- Self-Sabotage
- Negative Self-Talk
- Lack of Self-Compassion
My insightful Washington-state music teaching colleague Lesley Moffat has written an excellent book, I Love My Job But It’s Killing Me – The Teacher’s Guide to Conquering Chronic Stress and Sickness, and in my opinion, she hits the nail squarely on the head embracing Shakespeare’s “to thine own self be true” in a renewed motivation on self-help:
You must take care of yourself first. This is the hardest lesson of all, yet it is so important. Chances are you got where you are because you ran yourself ragged taking care of other people’s needs. I bet you never said no to requests to be on one more committee, drive carpool, watch a friend’s kids, and every other favor someone made of you, yet I’d also bet there’s a good chance you never take the time to take care of your own needs. When was the last time you read a book for fun? Or went to a movie you wanted to see? Or pursued a creative endeavor that made you happy? Or any one of a million things you want to do? I bet it’s been a long time. ⏤ Lesley Moffat
It is time to take the plunge towards better personal health, wellness, and balance in your life. There are plenty of resources out there for you to peruse, but don’t just sit there and read them! DO THEM!
Get started today!
PKF
© 2025 Paul K. Fox









