by Katherine Langford
We welcome this month’s guest blogger, Katherine Langford, who describes herself as “a digital marketing consultant, writer, freelancer, WordPress enthusiast, and coffee lover.” Thank you, Katherine! PKF
Music education has transformed dramatically in recent years. Traditional classrooms and rigid lessons are giving way to creative, flexible learning models that blend technology, collaboration, and real-world experience. The new model for modern music education isn’t just about mastering an instrument anymore—it’s about nurturing creativity, adaptability, and digital fluency.
Whether you’re a teacher, a student, or a parent trying to understand this shift, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the new model for modern music education and how it’s reshaping the way we learn, teach, and perform music.
What Defines the “New” Model for Modern Music Education?
The new model for modern music education is built on accessibility, inclusivity, and innovation. In the past, learning music often required private lessons, expensive instruments, and long practice hours under strict instruction. Now, technology has made learning more interactive, affordable, and engaging.
This model integrates online platforms, digital tools, and peer learning to create a dynamic environment. Students can watch video tutorials, join virtual ensembles, or even receive online class help from experienced musicians. It allows learners to progress at their own pace while receiving instant feedback and guidance.
Another major shift is the focus on creativity over perfection. Instead of emphasizing technical mastery alone, educators now encourage improvisation, digital composition, and personal expression. This approach builds confidence and helps students connect emotionally with their craft.
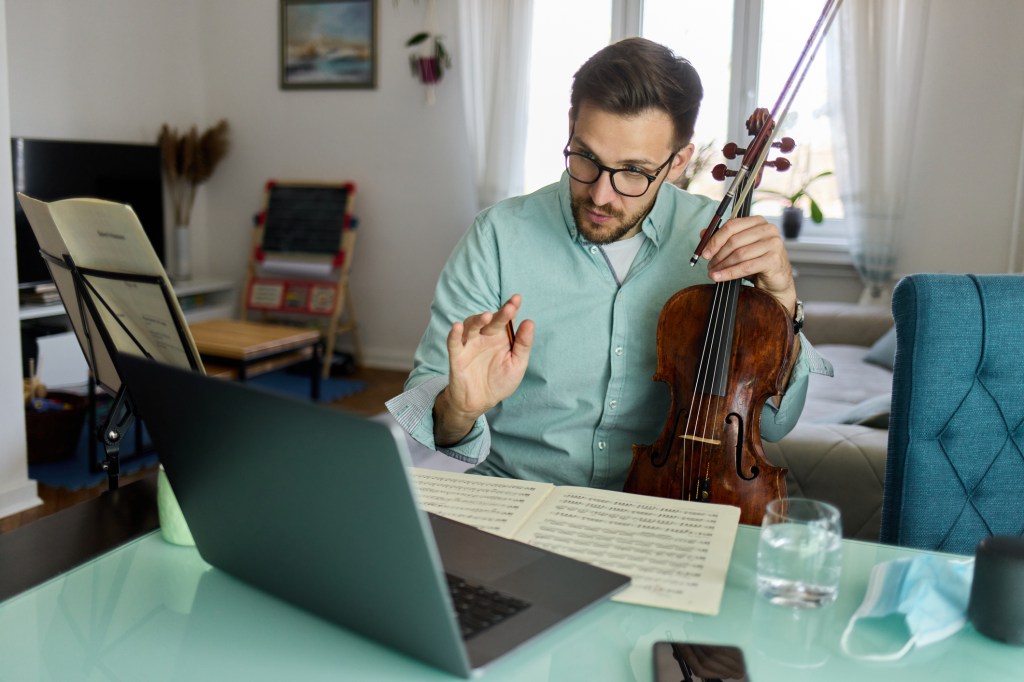

The Rise of Online Learning in Music Education
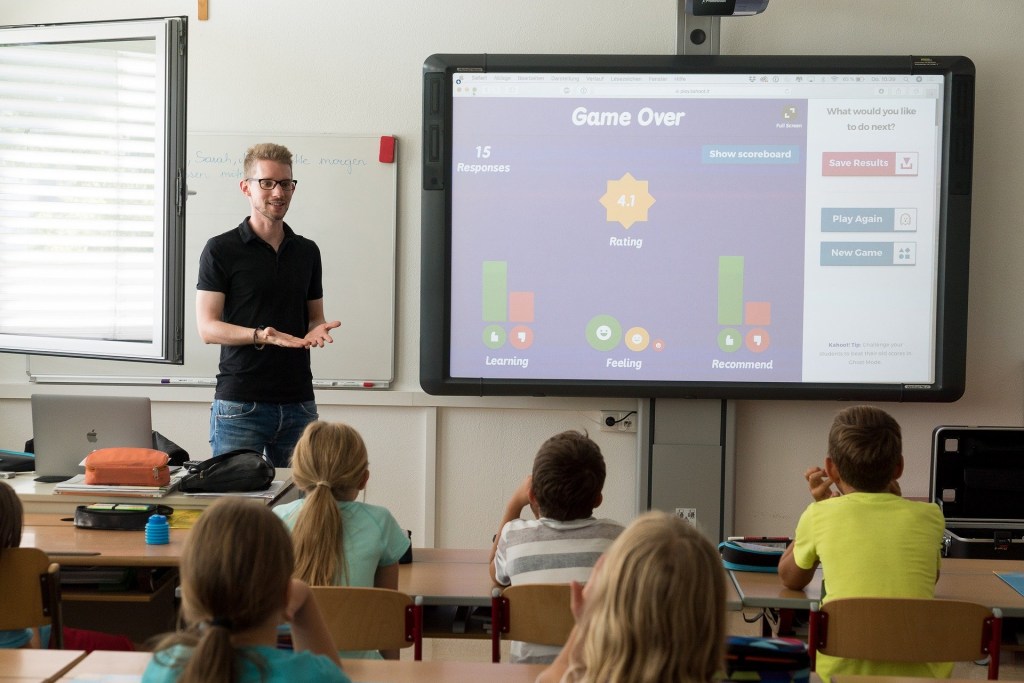
Online learning has become a cornerstone of modern music education. With platforms like YouTube, MasterClass, and specialized e-learning sites, anyone can access lessons from world-class musicians. Students can now learn piano, guitar, singing, or music production without leaving home.
These online classes are highly interactive, offering personalized feedback and practice tools. Some programs include live sessions, enabling real-time interaction with instructors and classmates. The flexibility to study from anywhere attracts learners of all ages and skill levels.
Online music education also supports busy professionals and students balancing multiple commitments. Many ask, Can I take my online class for music while working full-time? The answer is yes. With self-paced modules, recorded lessons, and flexible scheduling, anyone can continue learning without disrupting daily life.
Key Features of Modern Music Education
The new model for music learning focuses on a few core features that make it different from traditional instruction.
1. Technology Integration
Modern classrooms use music software, apps, and digital instruments. Tools like GarageBand, Ableton Live, and Sibelius help students compose, record, and edit their music. This hands-on digital experience prepares them for real-world music careers.
2. Collaboration and Global Access
Students can collaborate with others worldwide through online jam sessions or group projects. This exposure broadens cultural understanding and inspires new creative styles.
3. Personalized Learning Paths
AI-driven platforms now assess student progress and customize lesson plans. Learners receive targeted exercises that focus on areas needing improvement. This keeps motivation high and ensures steady progress.
4. Performance and Portfolio Building
Instead of graded recitals, students can build online portfolios, showcasing their songs or performances. This practical experience helps them prepare for music schools or careers in the industry.

Why Modern Music Education Matters Today
Music education today goes beyond traditional training. It prepares students for an evolving creative economy where adaptability and digital literacy matter.
The new model equips students with real-world skills such as sound design, audio editing, and digital marketing for music. These are essential for anyone pursuing a career in the modern music industry.
Additionally, it nurtures emotional intelligence. Creating and performing music helps students manage stress, improve focus, and build resilience. These soft skills translate into better academic and personal outcomes.
Another reason this new approach matters is its inclusivity. Learners who once couldn’t access quality lessons due to location or cost can now participate through online classes. Music education is no longer limited to elite institutions—it’s open to everyone.
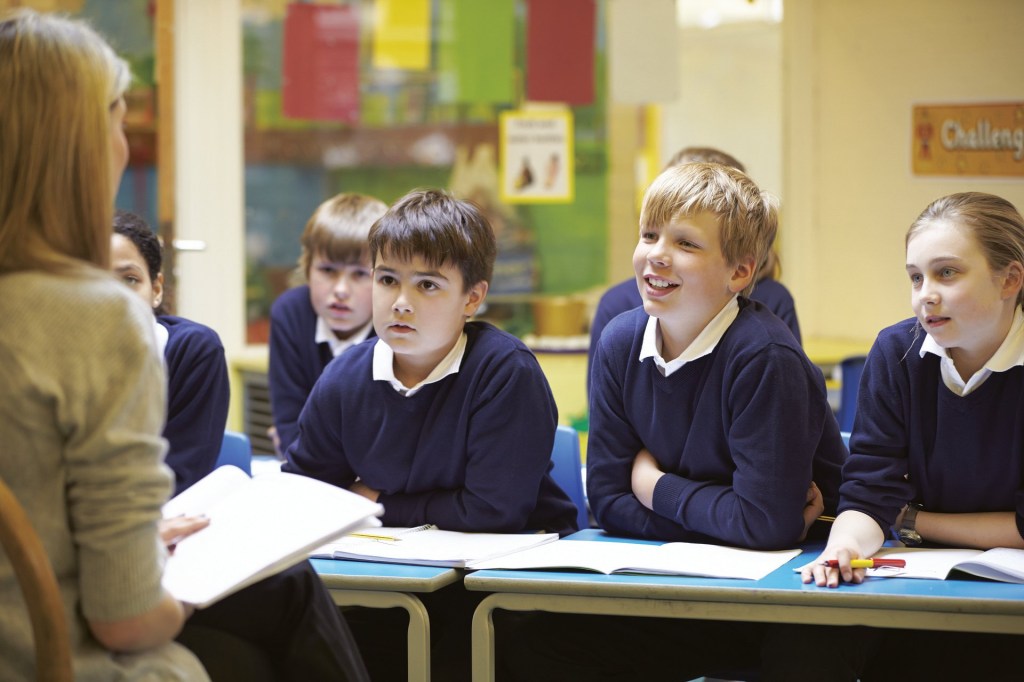
The Role of Teachers in Modern Music Education
Teachers remain at the heart of music education, but their role has evolved. Instead of being strict evaluators, they now act as mentors, facilitators, and collaborators.
Educators guide students through self-directed learning, helping them explore interests while mastering key concepts. They encourage experimentation and critical thinking rather than rote memorization.
Teachers also integrate multimedia tools into lessons, using interactive notation software, metronome apps, and virtual instruments. This keeps learning engaging and relevant.
Modern instructors understand that today’s learners consume music differently. They balance traditional techniques with contemporary styles, helping students connect classical foundations to genres like pop, jazz, or digital soundscapes.

The Impact of Technology on Music Learning
Technology has completely reshaped how music is created and taught. From recording studios to smartphone apps, innovation drives engagement and creativity.
Students can record, mix, and share their music instantly. They can join online communities, collaborate virtually, or receive detailed feedback through smart analysis tools.
Some schools use virtual reality to simulate live performance environments. This helps students overcome stage anxiety and refine their skills before performing in real-life situations.
Moreover, digital sheet music platforms make learning more interactive. Instead of flipping pages, learners can annotate, loop sections, and practice efficiently.
Technology also enables inclusive learning. Students with disabilities can use adaptive devices or apps that make instruments more accessible. This reinforces the principle that music truly belongs to everyone.
How Online Class Help Supports Music Learners
Many students struggle with consistency or technical challenges while learning online. That’s where online class help becomes valuable. Expert tutors assist learners in managing lessons, assignments, and projects.
They provide feedback, correct mistakes, and ensure students stay on track. This type of support bridges the gap between traditional mentoring and independent study.
For example, if a student is learning music theory but struggles with notation, they can seek online class help for one-on-one guidance. This approach ensures understanding without the stress of falling behind.
It’s especially useful for those pursuing formal music degrees remotely. Expert assistance ensures academic integrity while keeping the learning experience enriching.

Common Question: Is Online Music Education as Effective as In-Person Lessons?
Many learners wonder if virtual learning can match the impact of face-to-face instruction. The short answer is yes, it can be just as effective—sometimes even more.
Online music education offers flexibility and access to diverse expertise that local lessons may lack. You can study jazz composition with a teacher from New York or classical violin from a maestro in Vienna.
Additionally, digital lessons allow unlimited practice and playback. Students can review recorded sessions anytime, reinforcing understanding and mastery.
However, success depends on commitment and quality instruction. Active participation, consistent practice, and seeking feedback are key to thriving in online music education.
Challenges Facing the New Model for Modern Music Education
While modern approaches have many benefits, challenges still exist. Internet connectivity, lack of physical interaction, and screen fatigue can affect engagement.
Students may also struggle with motivation when learning alone. This is where teacher support and community involvement become crucial. Encouraging virtual collaborations and online performances helps maintain enthusiasm.
Another concern is access to instruments. Not every learner can afford quality equipment or digital tools. Schools and institutions need to bridge this gap by providing resources or scholarships for talented students.
Despite these obstacles, the benefits of digital and hybrid learning far outweigh the drawbacks. With ongoing innovation, these challenges are gradually being addressed.
The Future of Modern Music Education
The future of music education looks bright and interconnected. We’ll see more hybrid classrooms combining online and offline experiences. Students might attend physical rehearsals while collaborating digitally with international peers.
Artificial intelligence will continue shaping learning paths, analyzing performances, and suggesting improvements. Virtual and augmented reality will simulate live concerts and recording studios for immersive training.
Most importantly, inclusivity and creativity will remain the foundation of this evolving system. Every learner, regardless of background, will have the opportunity to express themselves musically.
The new model is creating musicians who not only play instruments but also understand technology, production, and storytelling. They’ll be ready to thrive in an industry that values both art and innovation.

How Students Can Get the Most Out of Modern Music Education
If you’re a student exploring the new world of music learning, here are some helpful tips:
- Set clear goals. Decide what you want to achieve before starting lessons.
- Stay consistent. Practice regularly, even if only for short sessions.
- Use technology wisely. Try apps, online lessons, and recording tools to track progress.
- Engage with others. Join online groups, perform live sessions, and exchange feedback.
- Seek guidance. Don’t hesitate to reach out for online class help when needed.
These small steps ensure that your learning remains enjoyable and productive.
The Cultural Shift in How We Value Music Education
In the past, music education was often viewed as a luxury. Today, it’s recognized as a vital part of cognitive and emotional development. Studies show that learning music improves memory, discipline, and communication skills.
The modern model has made music more inclusive, integrating it into mainstream education and digital life. Whether through school programs, online platforms, or personal study, students now see music as both an art and a skill for life.
Cultural acceptance has grown too. Parents now appreciate the value of creative subjects, realizing they develop critical thinking and empathy. This shift has expanded the reach of music education across age groups and professions.
Conclusion: Embracing the New Model for Modern Music Education
The new model for modern music education is more than just a trend, it’s a necessary evolution. It reflects how we live, learn, and connect in the digital age.
By combining technology, collaboration, and creativity, this approach empowers learners to explore their potential fully. Whether you’re learning to produce music, master an instrument, or compose original songs, the tools and opportunities are at your fingertips.
PKF
© 2025 Katherine Langford and Paul K. Fox
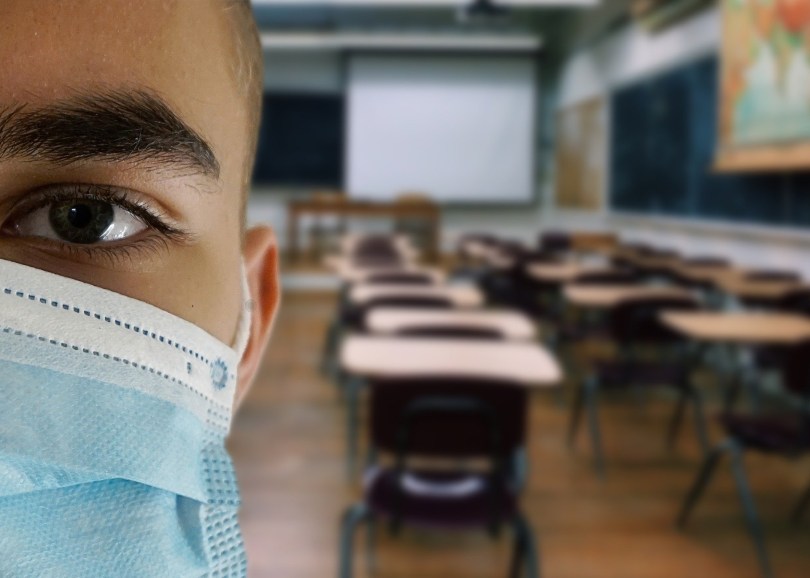




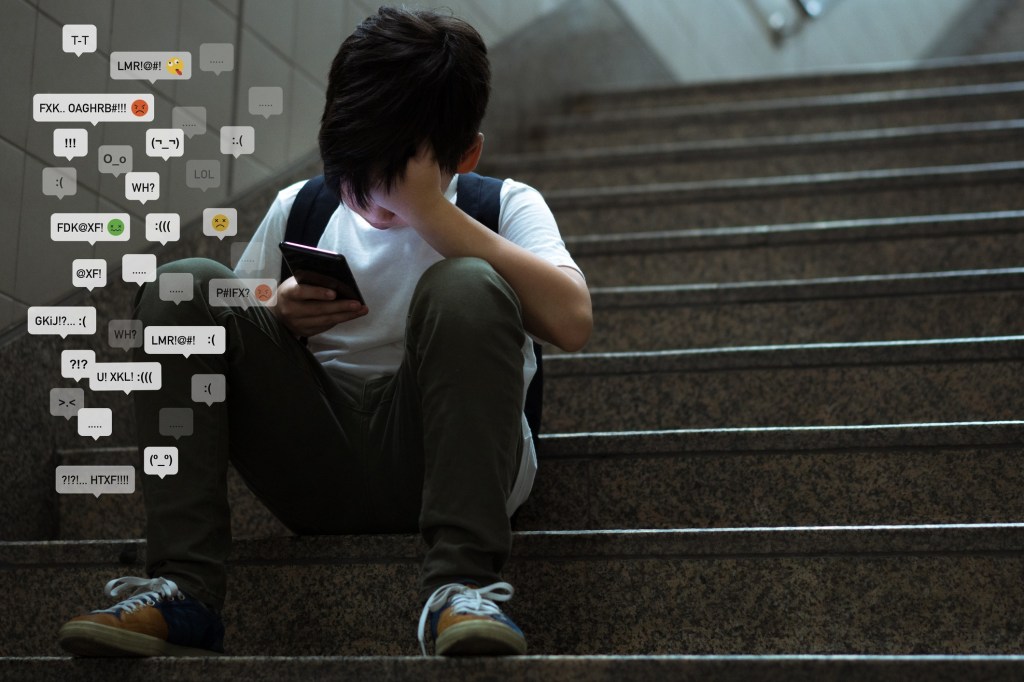

























 “Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”
“Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”



 For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc.
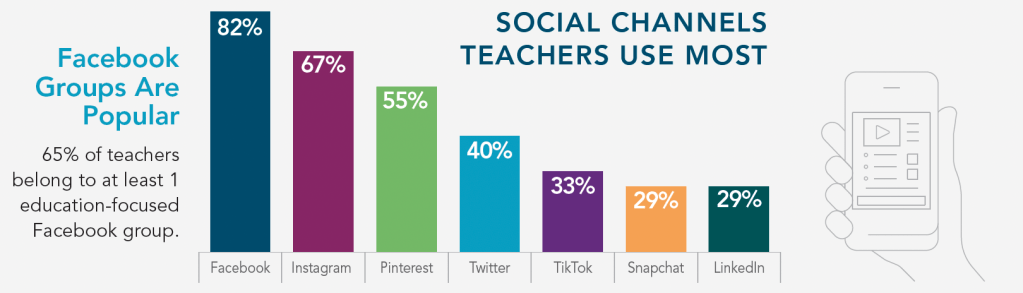
For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc. Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library
Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library  Five tips for coaching overwhelm:
Five tips for coaching overwhelm:

 “It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”
“It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”

 Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review
Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review  Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
