This is an introductory blog-post perusing my early research and resources on supporting educator health/wellness in advance to my presentation Self-Care Cookbook 2.0 – Recipes and Resources for School Leaders for the PA Department of Education’s SAS Institute 2025 state conference scheduled for December 8-10, 2025 in Hershey, PA. Here is the summary description for the workshop:

“Do you find the harried pace of our profession overwhelming and at times crushing when buried beneath decades of keeping our noses to the grindstone and putting everyone else’s needs above our own? Do some of your staff members say they are stressed out, constantly tired, plagued by one ailment after another, or wondering how they’re going to “keep up?” If health is interfering with your colleagues’ abilities to do their jobs and find success, balance, and meaning in their lives, then it is time for change. The purpose of this session is to empower school leaders and teachers with skills and attitudes needed to make informed decisions to promote self-improvements in their lifelong health and wellbeing, to LEARN tools for better time management and to help remediate fatigue, stress and burnout, CONNECT and collaborate with your staff to inspire unique strategies for better personal self-care, and ACTIVATE creative new approaches to foster an improved workplace environment.”
Actually, previous articles at this site have dived into this subject of educator stress, burnout, and the development of a health and wellness self-care plan to build resilience, work/life balance, and reignite our motivation and passion for teaching. For a complete overview, I recommend you revisit these:
- Teachers – Take Charge of Your Wellness (2025)
- Summer Reading (2021)
- Burned Out or Bummed Out? (2020)
- Teacher Self-Care During the Pandemic (2020)
- Stressed Out? (2020)
Always start with “THE WHY”
(Inspired by keynote speaker/author Simon Sinek): Why is this discussion so important now?


When I mentioned my research to my colleague (and former student) Dr. Timothy Wagner, Principal, Upper St. Clair High School (my former placement for full-time employment), he mentioned that this topic was timely and highly relevant, and suggested that perhaps there might be more statistics and resources “out there” on the stress of health-care workers and first-responders, which I found to be true. However, early looks have shown numerous parallels to the information in my 2023 Self-Care session.

My PDE SAS Institute session will become a “two-for-one” presentation, including the opportunity for school/system leaders, building administrators, and directors of school district professional development to also download my original “Self-Care Cookbook” (1.0) slides, recently updated for the DCMEA Annual State Conference (January 20, 2026). This self-help workshop is geared for educators to “on-their-own” explore strategies, implement use of individualized tools/remedies, and formulate new goals to improve health and wellness. Both sessions hope to cover these key questions:
- Why is it essential to personal health to achieve balance in our lives, and how can we achieve it?
- How does dedication to wellness lower the risk of illness, injury, and the quality of a person’s life?
- What are the consequences of our choices in terms of time and stress management?
- How do effective decision-making skills and goal setting influence healthier lifestyle choices?
- What are suggestions, strategies, and samples for the development of a personal self-care plan?
Using a facsimile of a prescription pad in Self-Care 1.0, I posed these personal reflections:
- How do I usually feel daily throughout the school year?
- What are the emotional and physical tolls of my job?
- What specific self-care activities do I need to incorporate to recharge and prevent burnout?
- What boundaries do I need to set around my work to honor personal time?
- What support systems can I build and/or professional help should I seek to create a sustainable practice?
Good ideas…
How can school admins support their staff in dealing with the climbing incidences of health problems, teacher exhaustion, call-offs, evidence of burnout, and high turnover rate? Sorting through a compendium of online research, these recommendations for school leaders occur repeatedly:
- Probably should go without saying: Show high visibility (“be seen by all”), recognition, and know everybody’s name. This goes a long way in building a sense of belonging of the staff and students.
- Provide more time for breaks and planning. Engage teachers in problem solving teams to identify and implement substantive ways to give them more time. Examples: cutting back on testing and data analysis; holding fewer and shorter meetings; putting a hold on new academic initiatives while increasing mental health initiatives conducted by school-based mental health professionals; hiring individuals who can assist with administrative tasks; compensating teachers for extra work; protecting classroom time by minimizing interruptions; reducing teaching hours to allow for more prep time and follow-up time.
- Foster a supportive community through mentorship programs.
- Distill high-impact strategies into a handful of manageable priorities. Once the goals are set, give teachers specific time within the school day or week to focus solely on them.
- Communicate directly, clearly, and frequently. “Supportive administrators know that a teacher’s time is valuable and that administrative meetings compete with individualized education programs, data teams, professional learning committees, cross-curricular planning meetings, and much more. So if a meeting is only for sharing straightforward information, it can be an email instead. It’s not necessary to have a meeting simply because the schedule says that faculty meetings are in the cafeteria on Mondays.” – Edutopia: “4 Practical Ways Administrators Support Teachers”
- Treat teachers with respect like the professionals they are, increasing mutual trust by decreasing micromanagement or reducing unnecessary accountability documentation.
- Shadow multiple teachers to experience first-hand the reality of their typical day.
- Allow educators the option to attend meetings and professional development activities virtually.
- Involve teachers in the creation of targeted professional development activities that are the most meaningful for them.
- Ask teachers about what specific help they need to improve classroom management.
- Develop a plan (with the Board of Education?) to increase teacher compensation over time, taking into account that many administrative and clerical tasks that are now required of teachers might ultimately be delegated to less highly compensated individuals.
- Address staff performance issues on an individual basis rather than issuing global reprimands that don’t apply to most teachers.
- Implement policies that encourage work-life balance. For example, recognize measurable indications of quality teaching rather than behaviors that signal a “more is better” approach (always coming in early and staying late, volunteering for everything, talking about working all weekend to catch up, etc.).
- Support educators by acknowledging stress, providing professional development on self-care, and creating a culture where asking for help is normalized.
- Ask teachers what mental health or other supports they need to cope with their own distress. Research has demonstrated the effectiveness of introducing trauma-informed strategies, including an emphasis on compassion fatigue and secondary trauma, as well as mindfulness strategies that are part of institutionalized wellness routines.
- Provide “safe spaces” (SEL) where educators can express themselves without fear of being judged, and practice “Mindful Leadership” to connect with and listen to them. “Getting to know your teachers on a more personal level makes it easier to identify the best thing you can do to support them, even if teachers aren’t sure what they need. The goal should be making sure everyone made it to work okay and that they’re in good spirits and ready to tackle the day.” – 7 MINDSETS: “5 Ways Administrators Can Support SEL for Teachers”
- Counteract “toxic positivity” by acknowledging that teachers are hurting and need space to grieve the continued losses associated with the pandemic.

Bad ideas…
These strategies cited by Effective School Solutions will NOT help teachers in the long-term:
- While “wear your jeans to work” days and offering coffee and donuts occasionally are nice employee appreciation efforts, they do nothing to address the underlying issues.
- Offering one-shot seminars or newsletters with suggestions about individual self-care activities (breathing exercises, physical exercise, time for self, etc.) can inadvertently place further burdens on teachers, conveying the impression that they are responsible for both creating and addressing the stress that is structural in nature.
- Don’t conduct teacher surveys or focus groups about how to reduce teacher stress and then proceed to ignore their suggestions about what would make things better.
- Don’t assume that short bursts of extra time (e.g., ending a meeting early to give teachers more time) is useful. Small, unexpected pieces of free time do not help teachers catch up with work that requires concentration and focus.
- Don’t avoid difficult conversations to address the performance problems of individual teachers by making blanket statements/warnings to all teachers, most of whom are not engaging in the problem behavior.
“Be careful not to adopt a stance of “Toxic Positivity,” that is, a stance that accentuates the positive (“we are all in this together,” “we are strong,” “it could be worse,” “look on the bright side”) while invalidating the very real pain that everyone is experiencing. Denying or ignoring unpleasant emotions tends to make them worse, not better.
– Effective School Solutions
Free Downloads
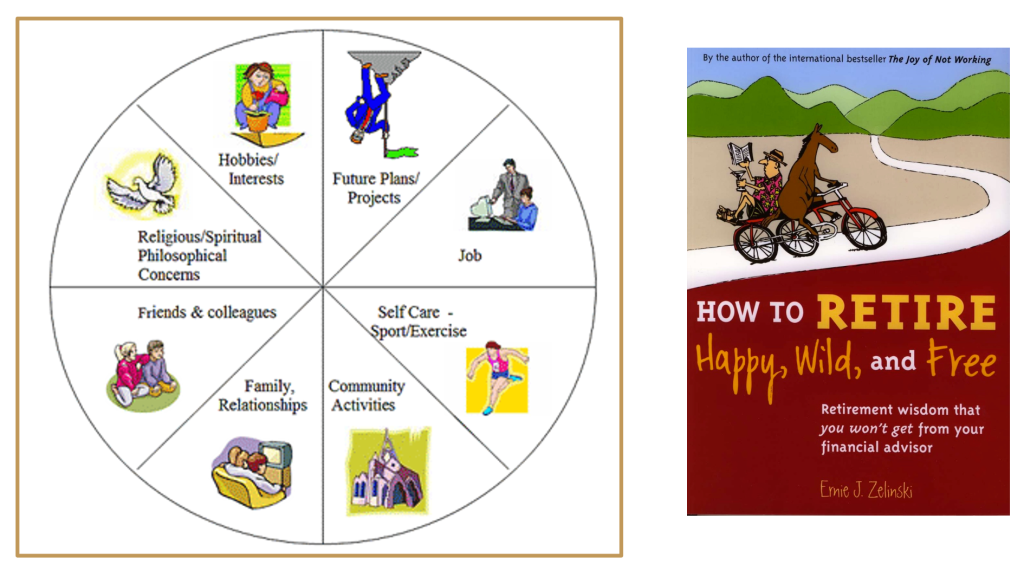
I am putting on the final touches to the SAS INSTITUTE 2025 Self-Care Cookbook 2.0 session, but have already assembled a huge bibliography of resources for your review (see below). For a “sneak preview” of my slide summary, click here. Future updates will be posted here: https://paulfox.blog/care/.
Better yet, register for the SAS Institute 2025 to see everything in person.

Sample Books
- 180 Days of Self-Care for Busy Educators by Tina H. Boogren, Solution Tree Press (2020)
- Awakened – Change Your Mindset to Transform Your Teaching by Angela Watson, Due Season Press & Educational Services (2023)
- The Balanced Band Director – Productivity and Wellness Tips to Amplify Your Impact, Not Your Workload by Lesley Moffat, Morgan James Publishing (2025)
- Demoralized – Why Teachers Leave the Profession They Love and How They Can Stay by Doris Santoro, Harvard Education Press (2018)
- Exhausted – Why Teachers Are So Tired and What They Can Do About It by Paul Murphy, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (2017)
- Fewer Things, Better by Angela Watson (2019)
- The Happy Teacher Habits by Michael Linsin, JME Publishing (2016)
- Love the Job, Lose the Stress: Successful Social and Emotional Learning in the Modern Music Classroom by Lesley Moffat (2022)
- Positive Mindset Habits for Teachers by Grace Stevens, Red Lotus 2018
- Rekindle Your Professional Fire – Powerful Habits for Becoming a More Well-Balanced Teacher by Mike Anderson, ASCD (2024)
- The Teacher’s Guide to Self-Care – Build Resilience, Avoid Burnout, and Bring a Happier and Healthier You to the Classroom by Sarah Forst, The Designer Teacher (2020)
- The Teacher’s Guide to Self-Care – The Ultimate Cheat Sheet for Thriving Through the School Year by Melanie J. Pellowski, Skyhorse Publishing (2020)
- Upbeat – Mindset, Mindfulness, and Leadership in Music Education and Beyond by Matthew Arau (GIA Publications (2022)
- The Weekend Effect: The Life-Changing Benefits of Taking Time Off and Challenging the Cult of Overwork by Katrina Onstad, HarperOne (2024)
Sample Websites
- https://7mindsets.com/5-ways-administrators-can-support-sel-for-teachers
- https://www.newleaders.org/blog/how-school-leaders-can-create-the-conditions-to-support-teacher-self-care
- https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/
- https://cea.org/burnout-is-real-98-of-teachers-better-pay-treatment-needed-now/
- https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/education/self-care-for-educators-guide/
- https://effectiveschoolsolutions.com/why-are-teachers-quitting/
- https://www.eschoolnews.com/sel/2023/09/22/teacher-burnout-solutions/
- https://www.edutopia.org/article/4-practical-ways-administrators-support-teachers/
- https://nafme.org/teacher-burnout-is-real-signs-and-how-to-avoid-it/
- https://www.talkspace.com/blog/self-care-for-teachers/
- https://www.edutopia.org/blog/5-tips-avoiding-teacher-burnout-mary-beth-hertz
- https://www.pbs.org/education/blogs/voices-in-education/the-3-rs-for-teacher-selfcare-reflect-release-recharge/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qPtsP7pBobI
- https://www.edweek.org/tm/articles/2014/05/20/ctq-pillars-signs-of-solutions-for-burnout.html
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/answer-sheet/wp/2014/12/12/teacher-the-day-i-knew-for-sure-i-was-burned-out/
PKF
© 2025 Paul K. Fox
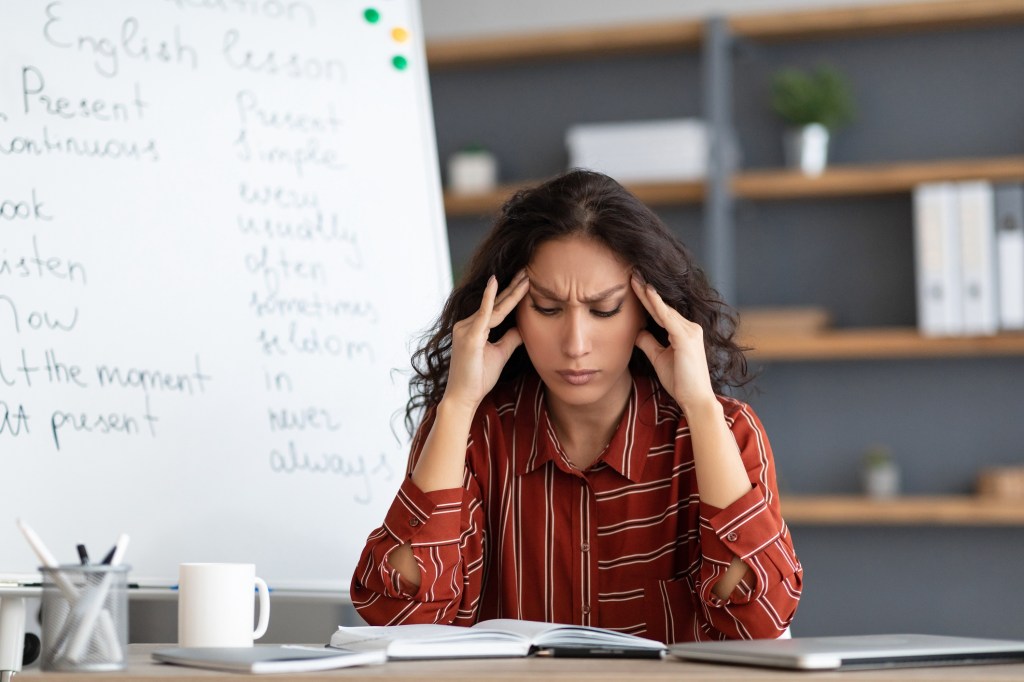



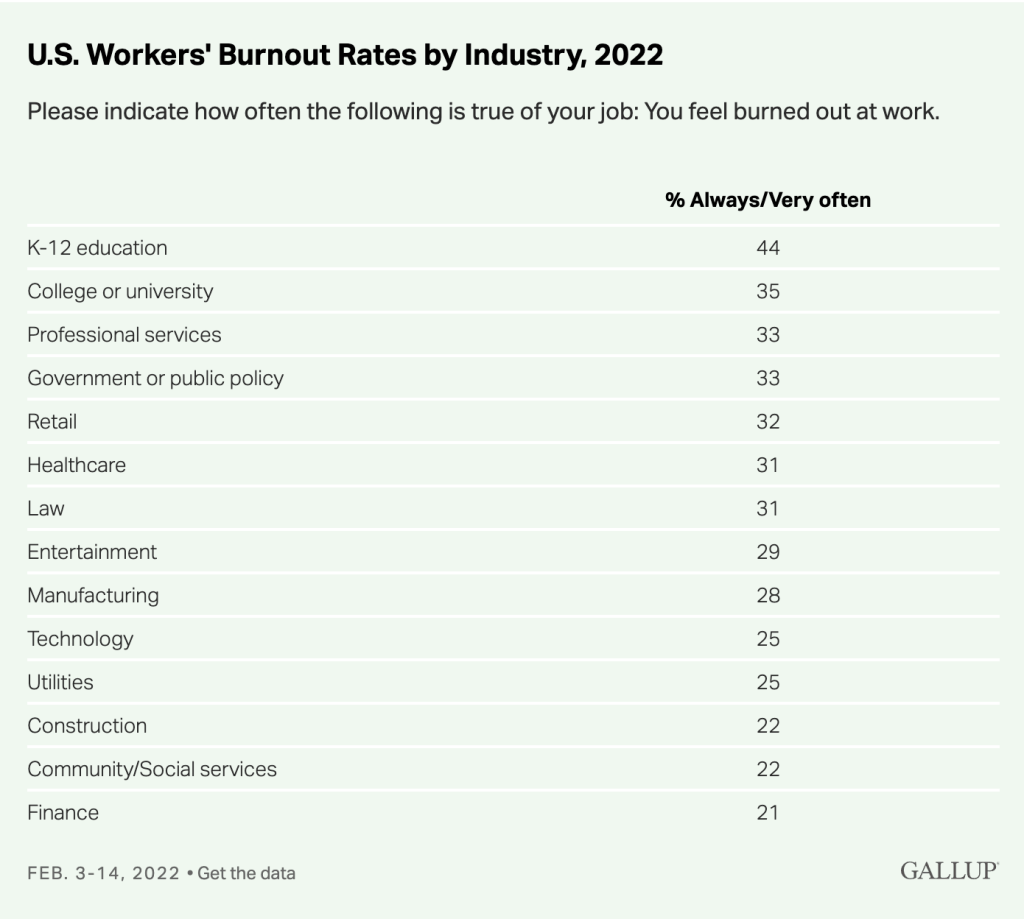




























 “Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”
“Our students are feeling it too. Typically, nationwide, one in three teenagers has experienced clinically significant anxiety in their lifetime (Merikangas et al., 2010). It’s probable that during a pandemic that heavily impacts everyday life, levels of anxiety in children and teens are even higher, and the possibility of subsequent trauma greater.”



 For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc.
For some, this has made matters worse… an “overload of abundance!” The multitude of venues and opportunities (too many unexplored “new technologies” for many of us baby-boomers!) included information about virtual ensembles, YouTube libraries, music games, lessons plans and platforms for synchronous and asynchronous e-learning, video-conferencing techniques, hardware and software reviews, etc. Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library
Go ahead and sign-up for a webinar or planned learning community meeting or two. Many professional development workshops are provided with “no extra fees” right now, like the NAfME library  Five tips for coaching overwhelm:
Five tips for coaching overwhelm:

 “It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”
“It’s hard to create a work-life balance when life is filled with work. Teachers are known for working long hours off-the-clock for no additional compensation. This is even more prevalent in music education. We add performances, competitions, musicals, individual lessons, fundraising, data entry, and even music composition and arranging to our task list.”

 Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review
Her book should be required reading for all music teachers, even retirees who want to remain active in the profession. (Read my previous review  Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:
Make self-care PRIORITY ONE for YOU! I know, you have heard all of these before:



 Focus
Focus

 Why even good days with your students leave you drained.
Why even good days with your students leave you drained.



 But then a group of British and dutch researchers asked an interesting question. They wondered if everyone had it backwards. Did the discomfort of physical fatigue cause the runners to think negatively, like everyone assumed, or did the runners negative thoughts make them more physically tired and sore? It was a chicken and egg question.
But then a group of British and dutch researchers asked an interesting question. They wondered if everyone had it backwards. Did the discomfort of physical fatigue cause the runners to think negatively, like everyone assumed, or did the runners negative thoughts make them more physically tired and sore? It was a chicken and egg question.
 6:30 a.m. an hour of cardio
6:30 a.m. an hour of cardio sake of the music program, add a new ensemble, schedule after-school time to teach a solo or instrumental part, and plan more weekend and evening “learning activities” or events beyond the scope of most other academic subject teachers. It was not unusual for me to be at school by 6:45 a.m., eat lunch in my car on the way to my second or third assignment as an itinerant, stop for a quick “date” and dinner out with my wife, return to school for band, orchestra, or musical practices, and not get home until 9 or or 10 p.m. As a retiree, I now ask, “What ever happened to all of this stamina and endurance?” Pushing wheel chairs only four hours a day three times a week at a local hospital, I sometimes find myself wanting to take a “power nap” when I get home! Never you fear: the healthy “calendar of a retired music teacher” is as busy (and hectic) as full-time employment… We always say, “I wonder how I ever had the time to do all of these things and work at the same time!”
sake of the music program, add a new ensemble, schedule after-school time to teach a solo or instrumental part, and plan more weekend and evening “learning activities” or events beyond the scope of most other academic subject teachers. It was not unusual for me to be at school by 6:45 a.m., eat lunch in my car on the way to my second or third assignment as an itinerant, stop for a quick “date” and dinner out with my wife, return to school for band, orchestra, or musical practices, and not get home until 9 or or 10 p.m. As a retiree, I now ask, “What ever happened to all of this stamina and endurance?” Pushing wheel chairs only four hours a day three times a week at a local hospital, I sometimes find myself wanting to take a “power nap” when I get home! Never you fear: the healthy “calendar of a retired music teacher” is as busy (and hectic) as full-time employment… We always say, “I wonder how I ever had the time to do all of these things and work at the same time!”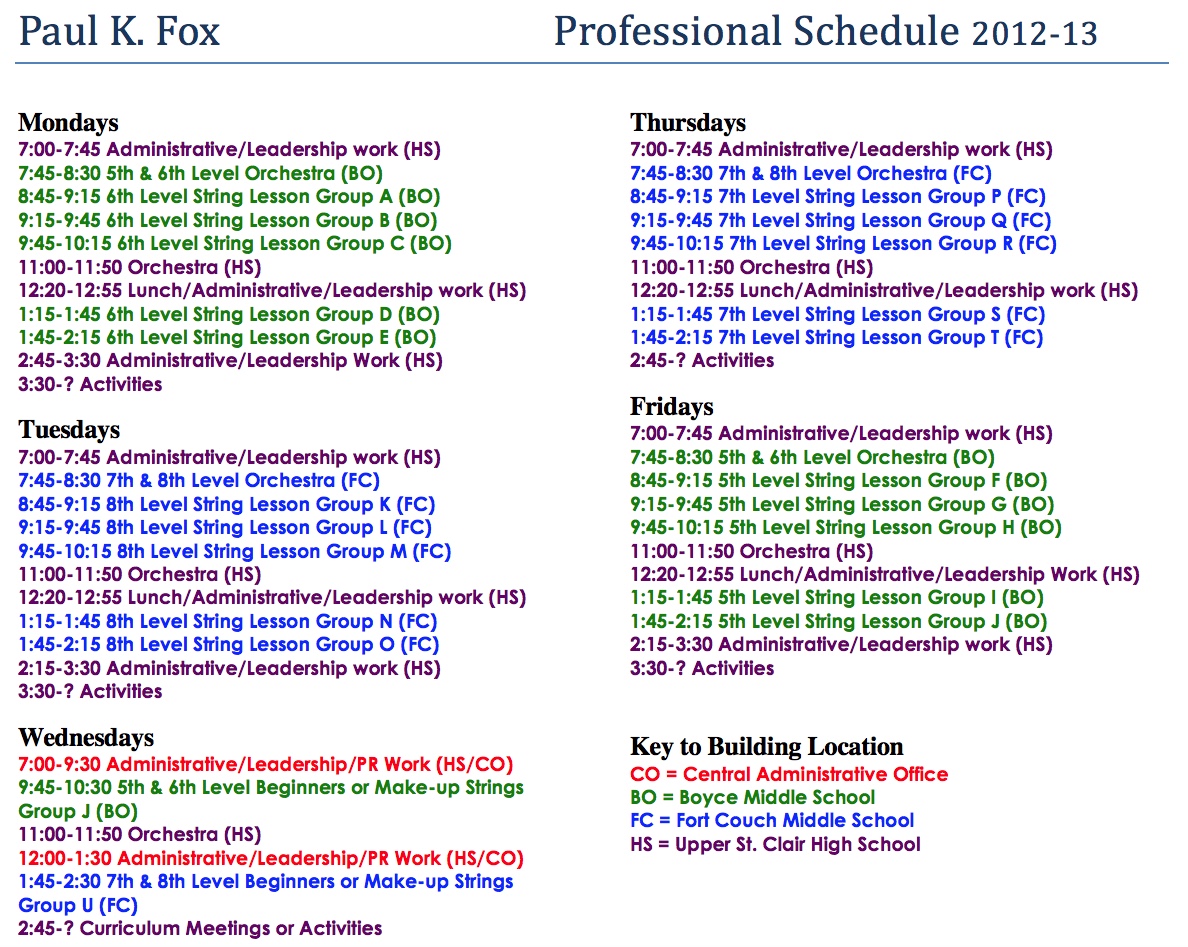









 Over the years, I have been a strong advocate of equal-access to music and the arts as an essential part the education of all children. This blog will give me an opportunity to put a lot of my thoughts in one place. I am aware that there are many people “out there” who offer the premise that studying music makes you successful in other areas, and you will see that this assumption is well-supported. However, I am not a brain scientist. I cannot confirm research that seems to point to a direct correlation that “the music itself makes us smarter.” It could be that students who are attracted to and become proficient in the arts are somehow uniquely “wired,” have a greater work ethic, or are better intellectually “equipped” to become successful engineers, doctors, lawyers, educators, scientists – you name the career – and enjoy life-long happiness and self-realization. So many of those music-in-our-schools-month fliers say “music is basic,” “music is math,” “music is reading,” “music is science,” etc. and they are right! So, it’s not wrong to bring it up. But we should be fully aware that the primary goal of an education in the arts is for the development of creative self-expression.
Over the years, I have been a strong advocate of equal-access to music and the arts as an essential part the education of all children. This blog will give me an opportunity to put a lot of my thoughts in one place. I am aware that there are many people “out there” who offer the premise that studying music makes you successful in other areas, and you will see that this assumption is well-supported. However, I am not a brain scientist. I cannot confirm research that seems to point to a direct correlation that “the music itself makes us smarter.” It could be that students who are attracted to and become proficient in the arts are somehow uniquely “wired,” have a greater work ethic, or are better intellectually “equipped” to become successful engineers, doctors, lawyers, educators, scientists – you name the career – and enjoy life-long happiness and self-realization. So many of those music-in-our-schools-month fliers say “music is basic,” “music is math,” “music is reading,” “music is science,” etc. and they are right! So, it’s not wrong to bring it up. But we should be fully aware that the primary goal of an education in the arts is for the development of creative self-expression.
 the one who had the greatest influence on my going into a career of music teaching was Eugene Reichenfeld, who I saw the last period of every day in Orchestra at Penn Hills HS, at least once a week in a private lesson and rehearsals of the Wilkinsburg Civic Symphony on Thursday nights, and over the three summers at the Kennerdell Music and Arts Festival in Venango County. What a role model! Partially blind and losing his hearing, Mr. Reichenfeld played violin, cello, and guitar, and taught uninterrupted until three weeks before he died at the ripe old age of 103!
the one who had the greatest influence on my going into a career of music teaching was Eugene Reichenfeld, who I saw the last period of every day in Orchestra at Penn Hills HS, at least once a week in a private lesson and rehearsals of the Wilkinsburg Civic Symphony on Thursday nights, and over the three summers at the Kennerdell Music and Arts Festival in Venango County. What a role model! Partially blind and losing his hearing, Mr. Reichenfeld played violin, cello, and guitar, and taught uninterrupted until three weeks before he died at the ripe old age of 103! Did your father ever realize why you chose music? In December 1986, Dad came to my choral/orchestra department production of Scrooge, involving over 250 students at my second career assignment, Upper St. Clair High School. After the closing curtain, he came up to me and asked, “Did you do all of this yourself? I answered, “Well, I had a lot of help. I did prepare the students on the dialogue parts in the script, the leads’ solos, chorus harmonies, and orchestra accompaniment, but I needed a drama specialist for coaching the actors and a choreographer for the dances. And yes, I am also the show’s producer, responsible for the printing of the program and tickets, finding people to assist in sewing the costumes, building the sets, running the stage tech, and applying the make-up.” After a short pause, he said something I will never forget: “Wow! This was incredible! You really made a difference to so many of your students’ lives.” He was proud of me, and finally expressed it! (It was a good thing too… he died suddenly of a heart attack exactly two years later when I was in the middle of staging USCHS’s Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat.)
Did your father ever realize why you chose music? In December 1986, Dad came to my choral/orchestra department production of Scrooge, involving over 250 students at my second career assignment, Upper St. Clair High School. After the closing curtain, he came up to me and asked, “Did you do all of this yourself? I answered, “Well, I had a lot of help. I did prepare the students on the dialogue parts in the script, the leads’ solos, chorus harmonies, and orchestra accompaniment, but I needed a drama specialist for coaching the actors and a choreographer for the dances. And yes, I am also the show’s producer, responsible for the printing of the program and tickets, finding people to assist in sewing the costumes, building the sets, running the stage tech, and applying the make-up.” After a short pause, he said something I will never forget: “Wow! This was incredible! You really made a difference to so many of your students’ lives.” He was proud of me, and finally expressed it! (It was a good thing too… he died suddenly of a heart attack exactly two years later when I was in the middle of staging USCHS’s Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat.)


 Musical (sound smart)
Musical (sound smart) Transforming the way schools should be run, the multiple intelligences theory suggests that teachers be trained to present their lessons in a wide variety of ways using music, cooperative learning, art activities, role play, multimedia, field trips, inner reflection, and much more. This approach truly “customizes the learning” and provides eight or more potential pathways to learning.
Transforming the way schools should be run, the multiple intelligences theory suggests that teachers be trained to present their lessons in a wide variety of ways using music, cooperative learning, art activities, role play, multimedia, field trips, inner reflection, and much more. This approach truly “customizes the learning” and provides eight or more potential pathways to learning.
 Innovation
Innovation

 The
The 





 The purpose of this short SHJO “Series to Share” is to get you started with some basic “how-to steps” to learn how to conduct. Truly, for success in directing an ensemble, the only thing you need to do is “give it a try” and practice those beat patterns with your favorite musical selections. During the Saturday SHJO rehearsals in December, we will give you the opportunity to direct the entire group and provide you a few hints!
The purpose of this short SHJO “Series to Share” is to get you started with some basic “how-to steps” to learn how to conduct. Truly, for success in directing an ensemble, the only thing you need to do is “give it a try” and practice those beat patterns with your favorite musical selections. During the Saturday SHJO rehearsals in December, we will give you the opportunity to direct the entire group and provide you a few hints! The mission of South Hills Junior Orchestra, which rehearses and performs at the Upper St. Clair High School in Pittsburgh, PA, is to support and nurture local school band and orchestra programs, to develop knowledge, understanding, performance skills, and an appreciation of music, to increase an individual member’s self-esteem and self-motivation, and to continue to advance a life-long study of music. Members of the Orchestra learn, grow, and achieve positions of leadership to serve their fellow members.
The mission of South Hills Junior Orchestra, which rehearses and performs at the Upper St. Clair High School in Pittsburgh, PA, is to support and nurture local school band and orchestra programs, to develop knowledge, understanding, performance skills, and an appreciation of music, to increase an individual member’s self-esteem and self-motivation, and to continue to advance a life-long study of music. Members of the Orchestra learn, grow, and achieve positions of leadership to serve their fellow members.